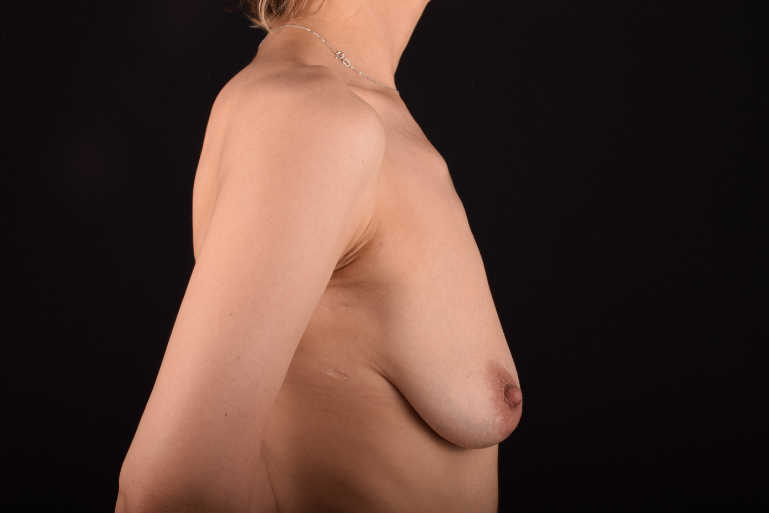
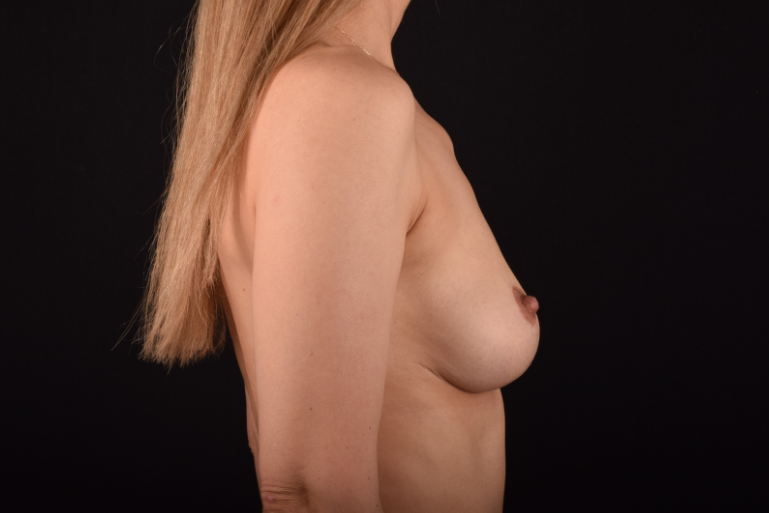
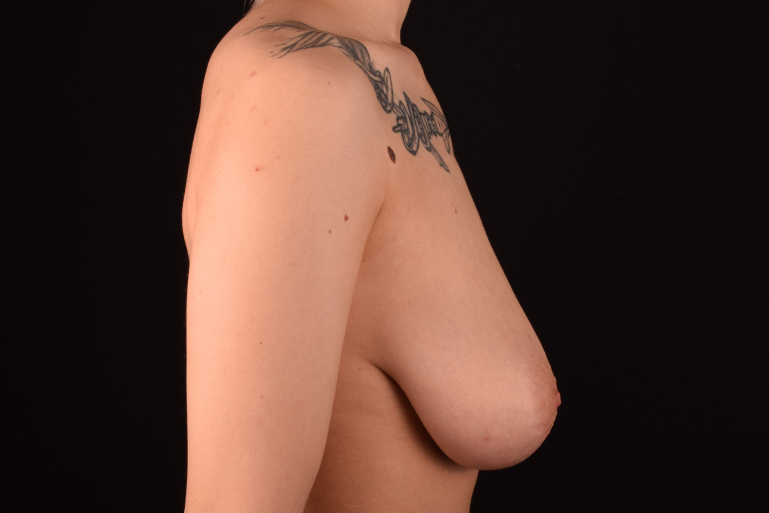
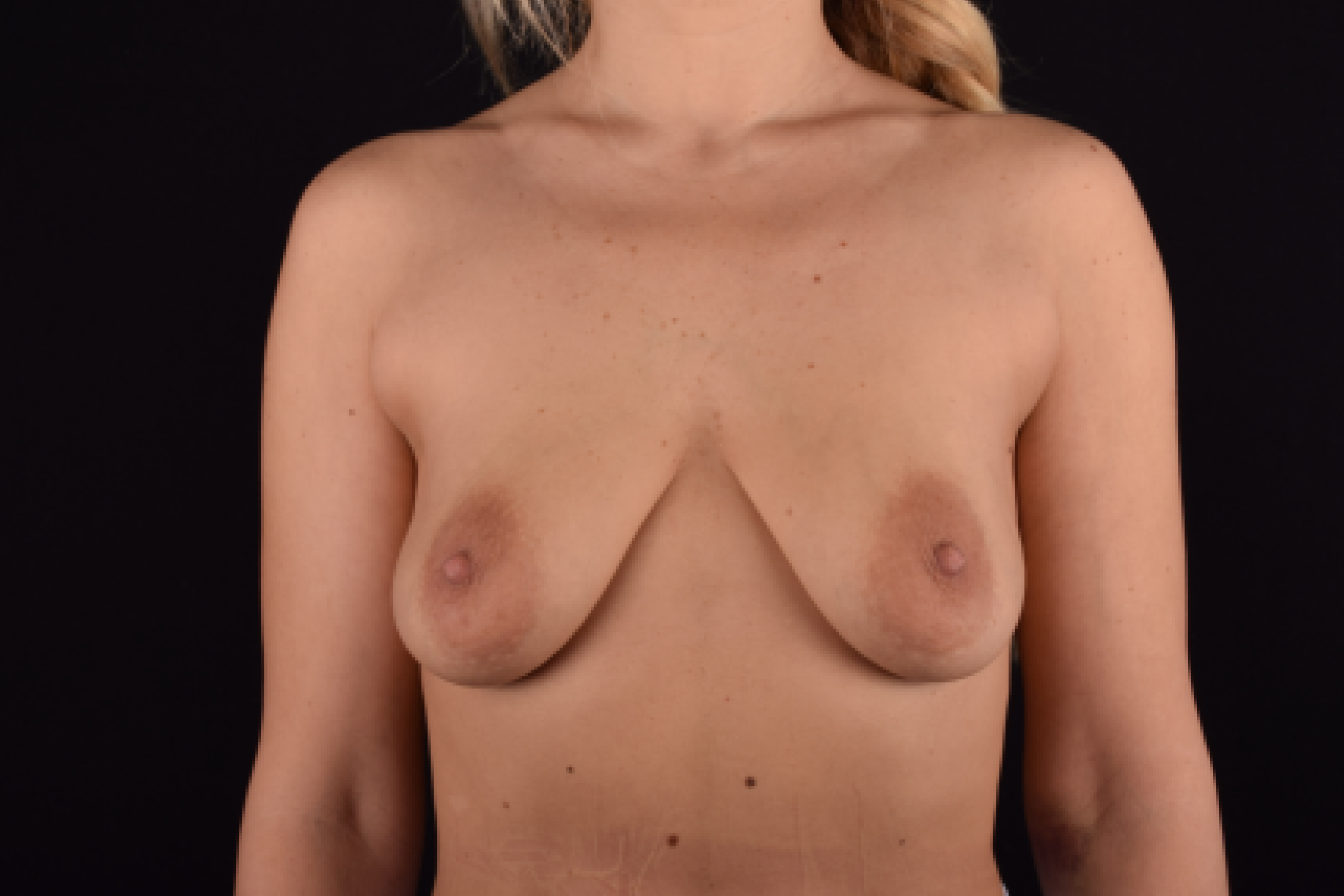
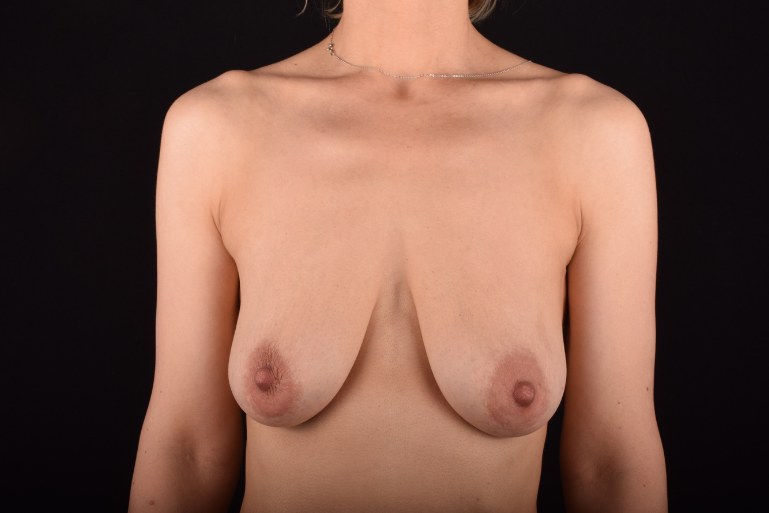
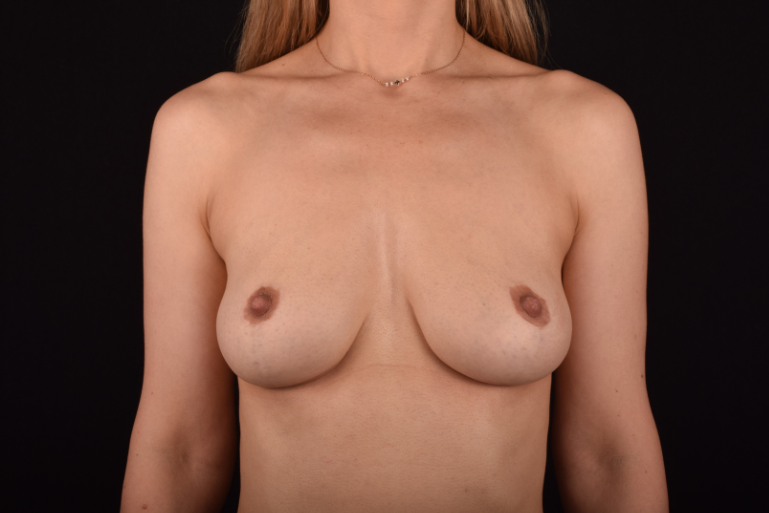
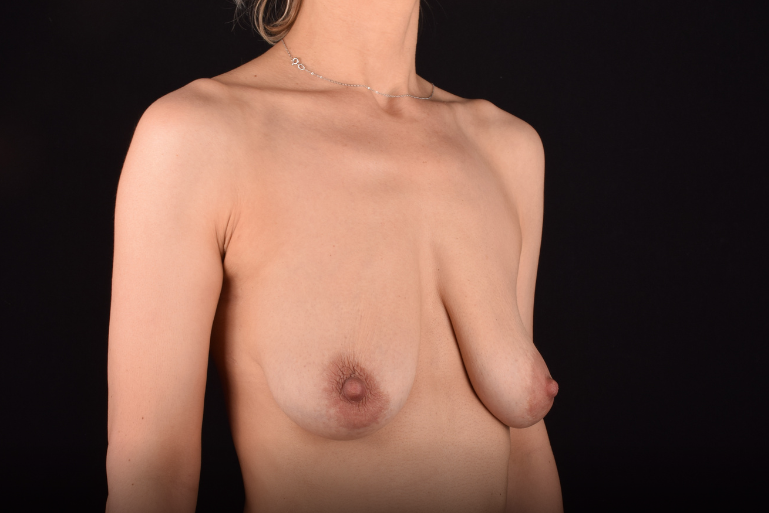
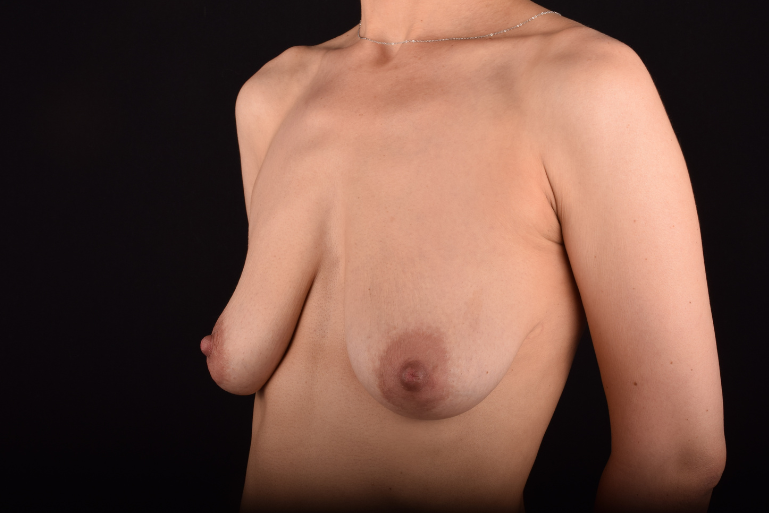
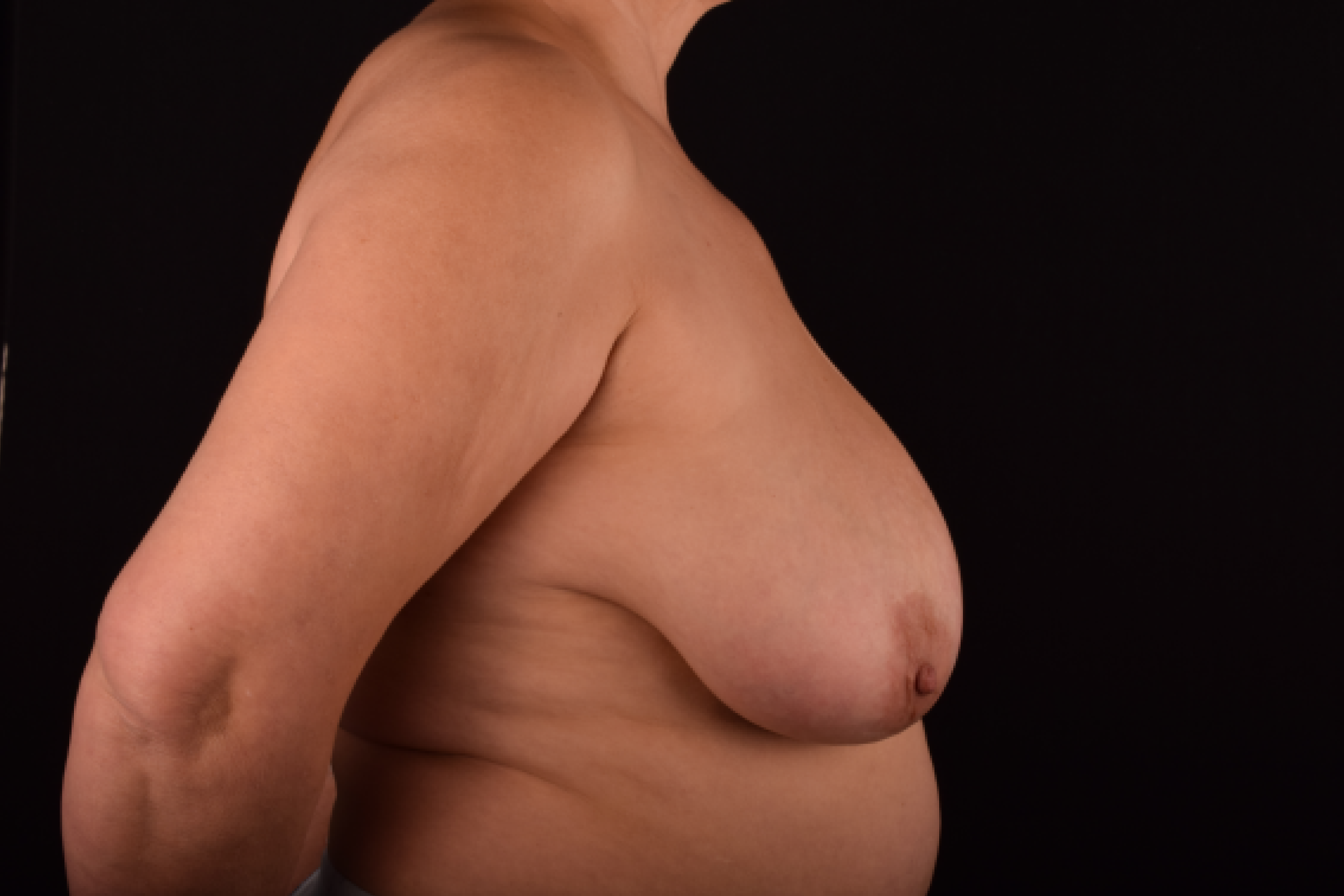
The most common causes of breast sagging (ptosis):
- After-effects of pregnancy and breastfeeding.
- Significant weight lose of a patient.
- Loss of breast elasticity due to the age-related changes.
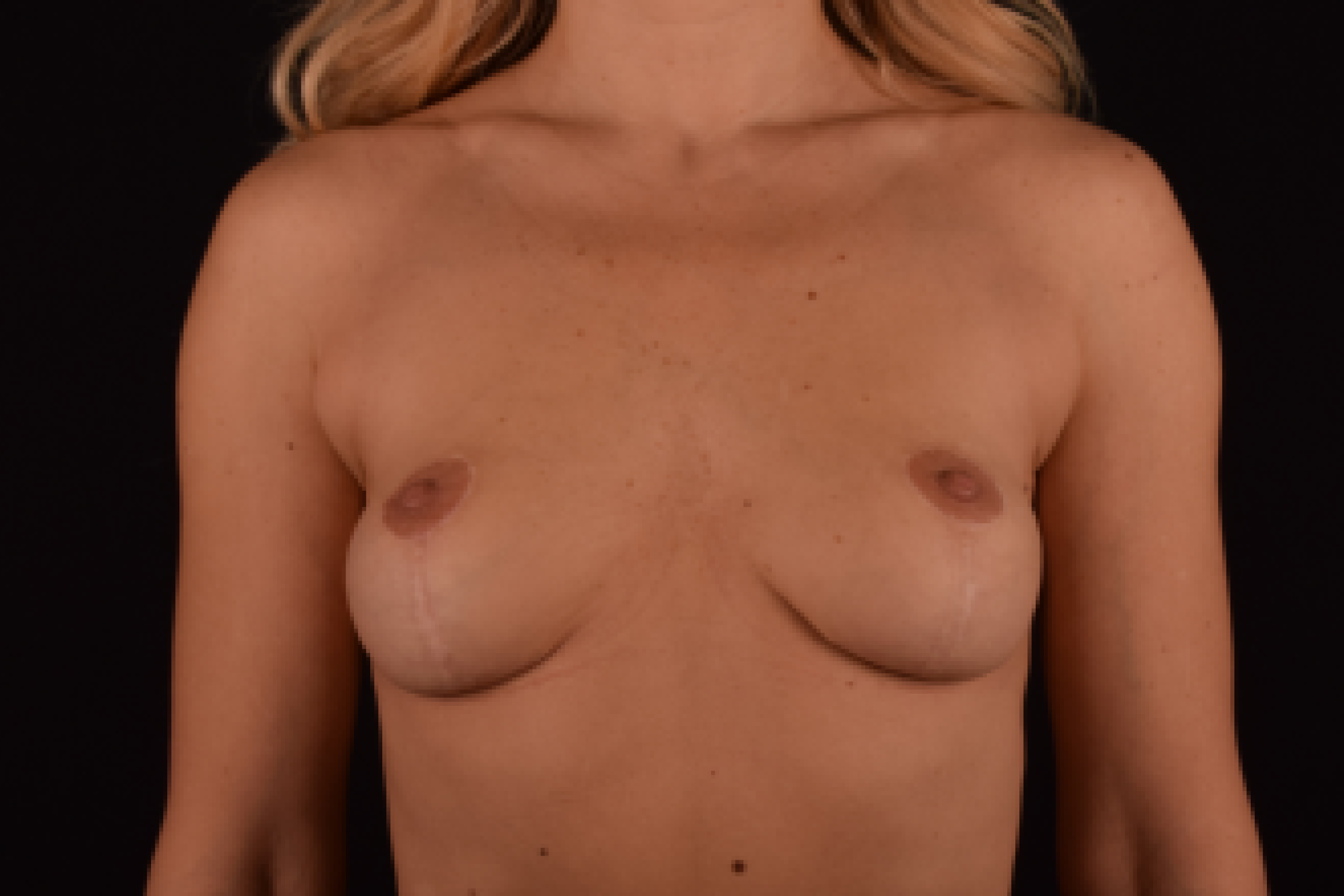
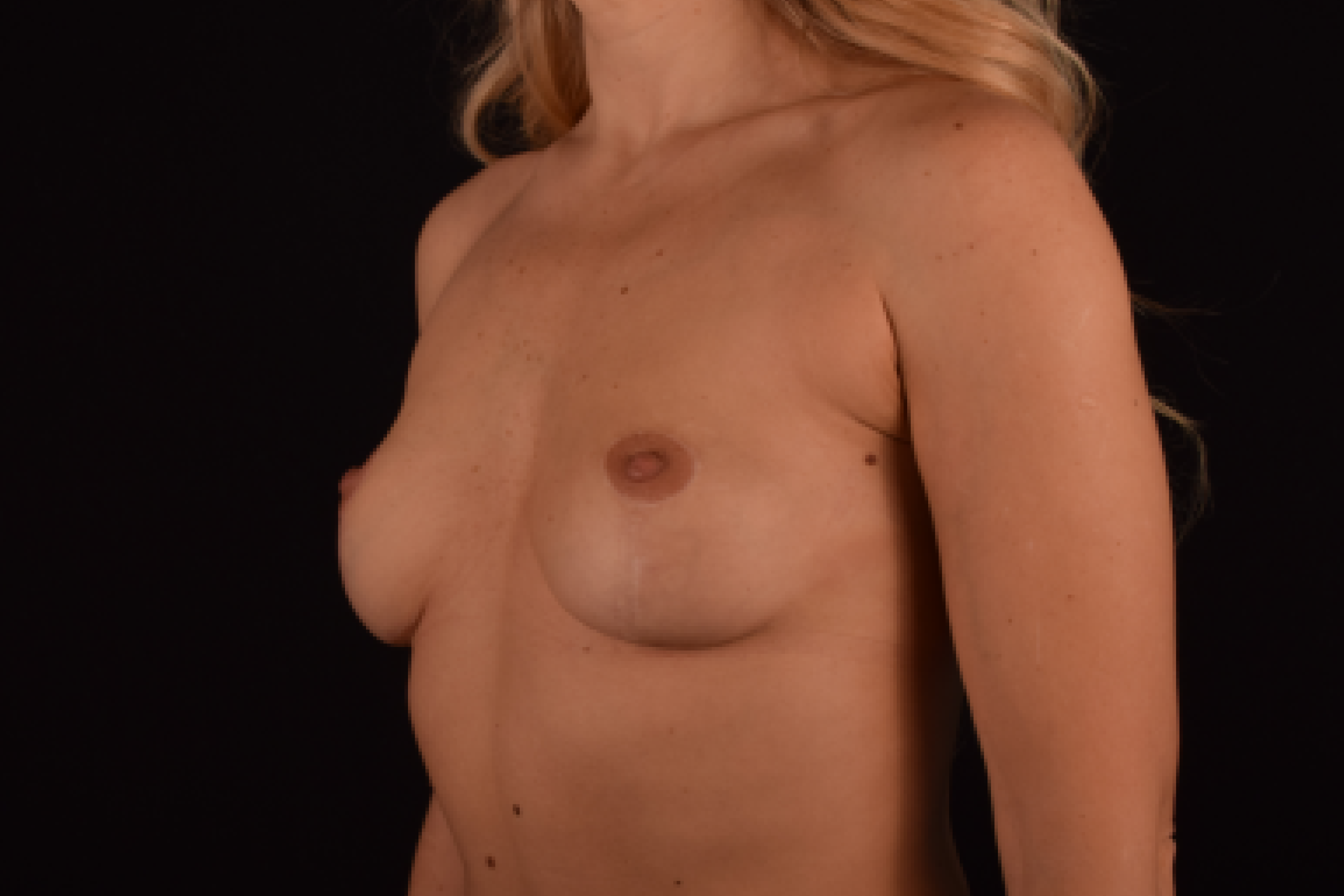
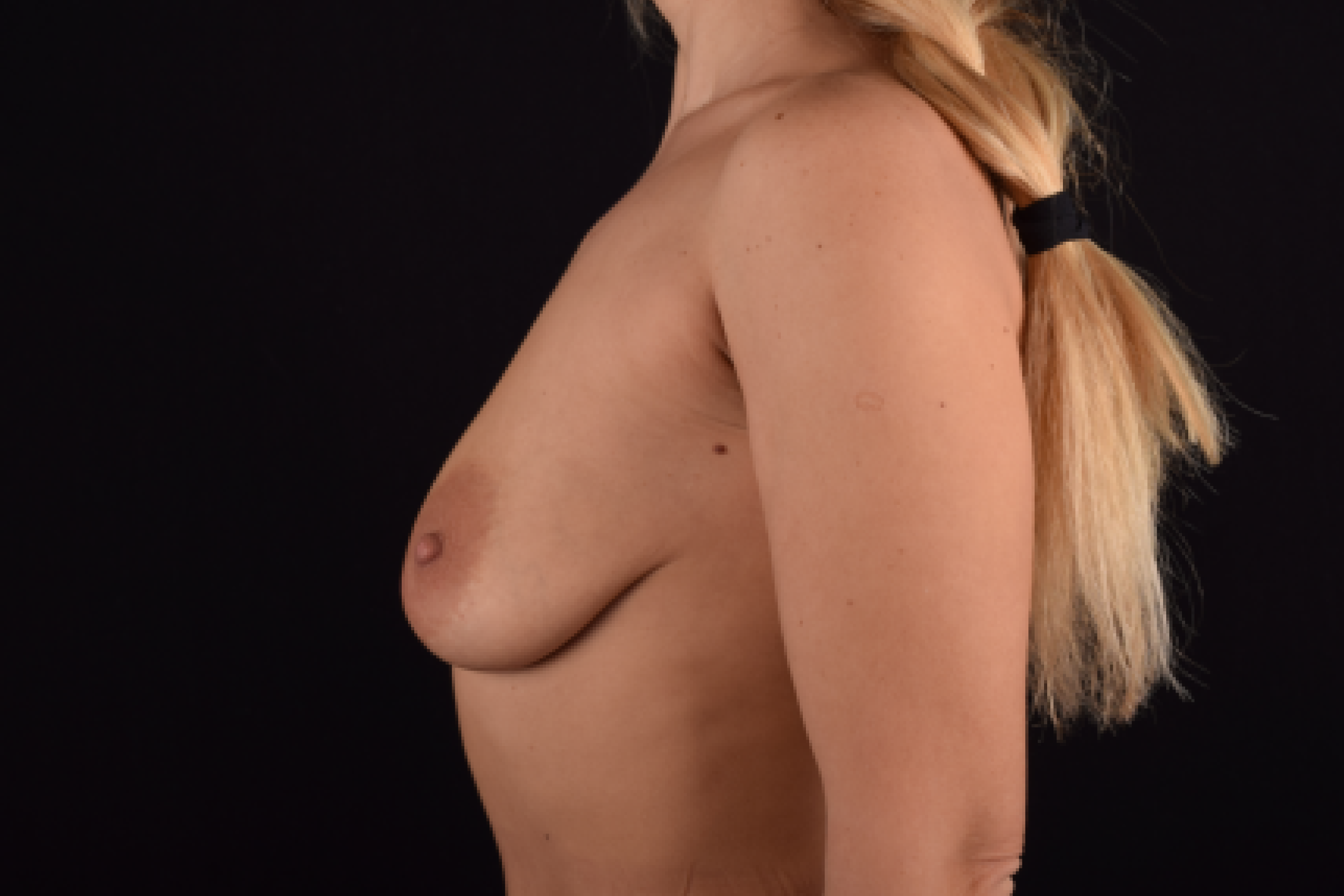
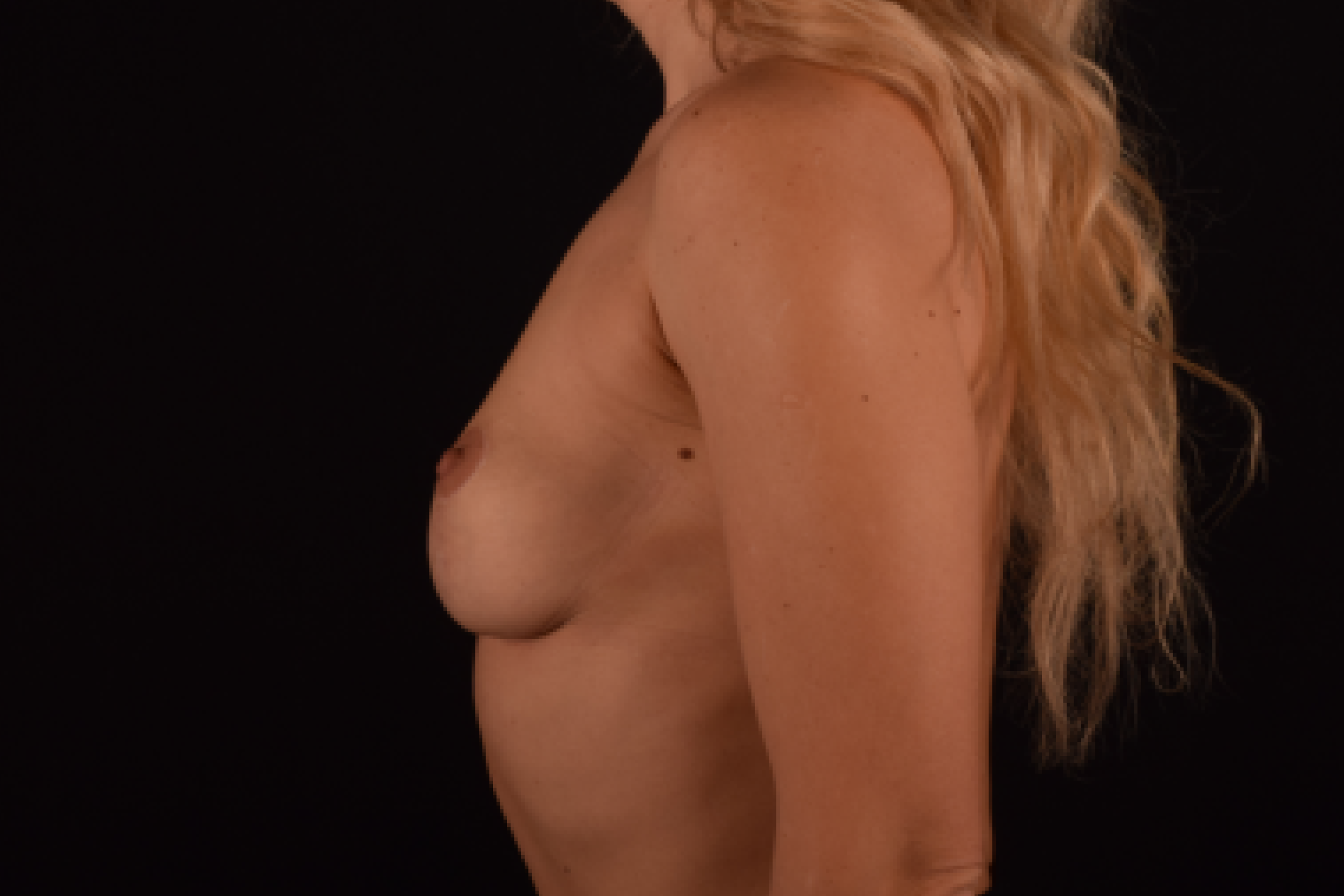
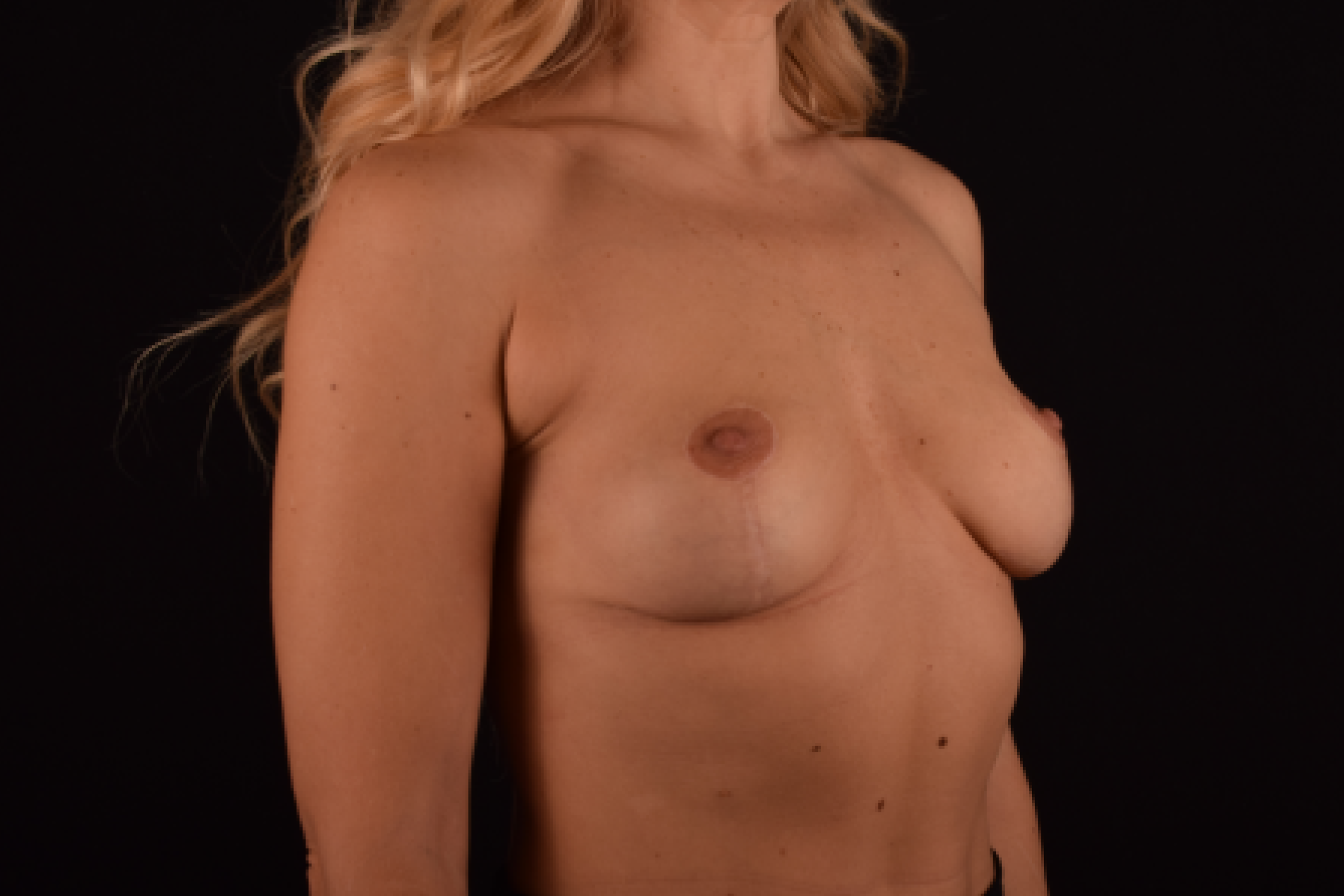
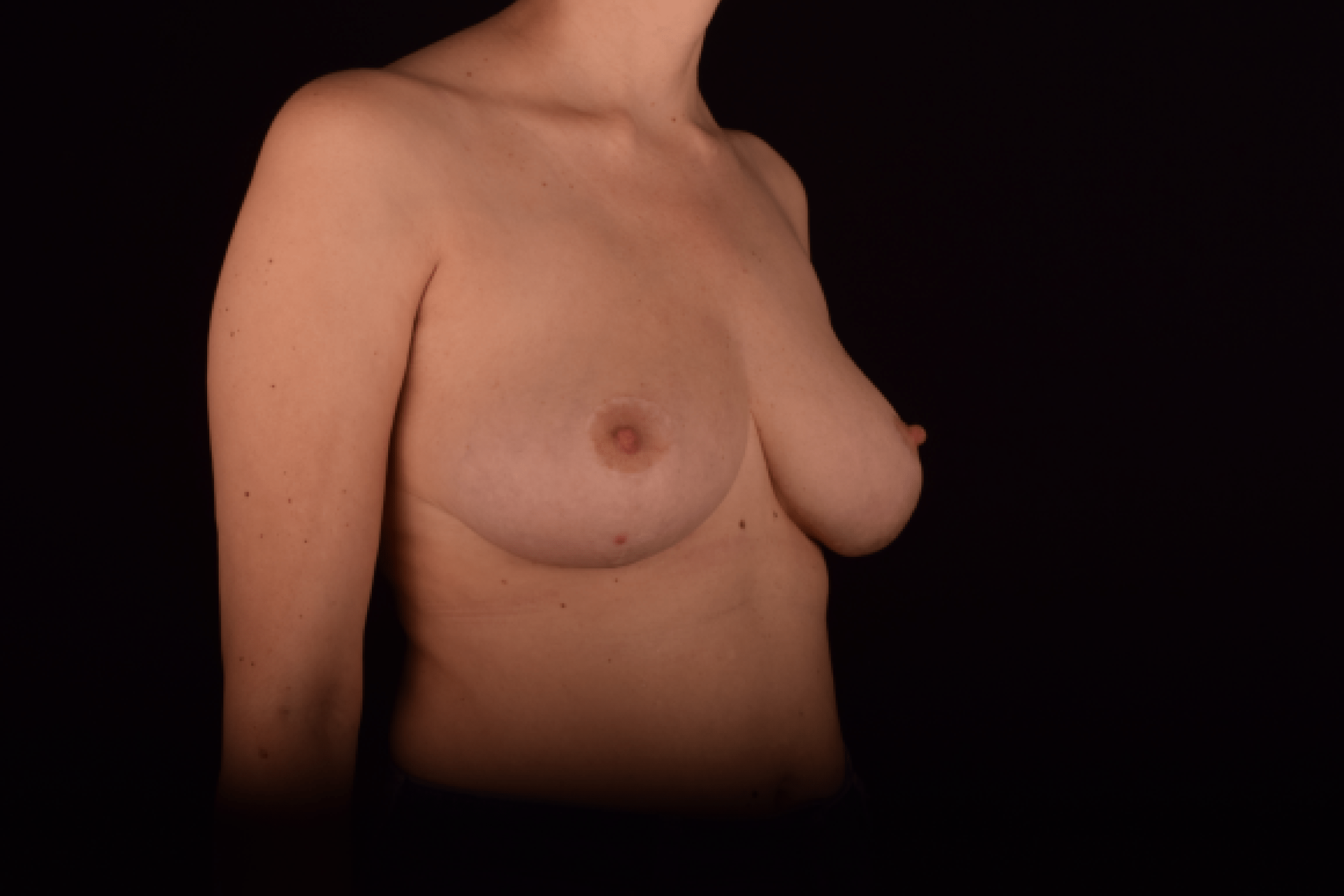
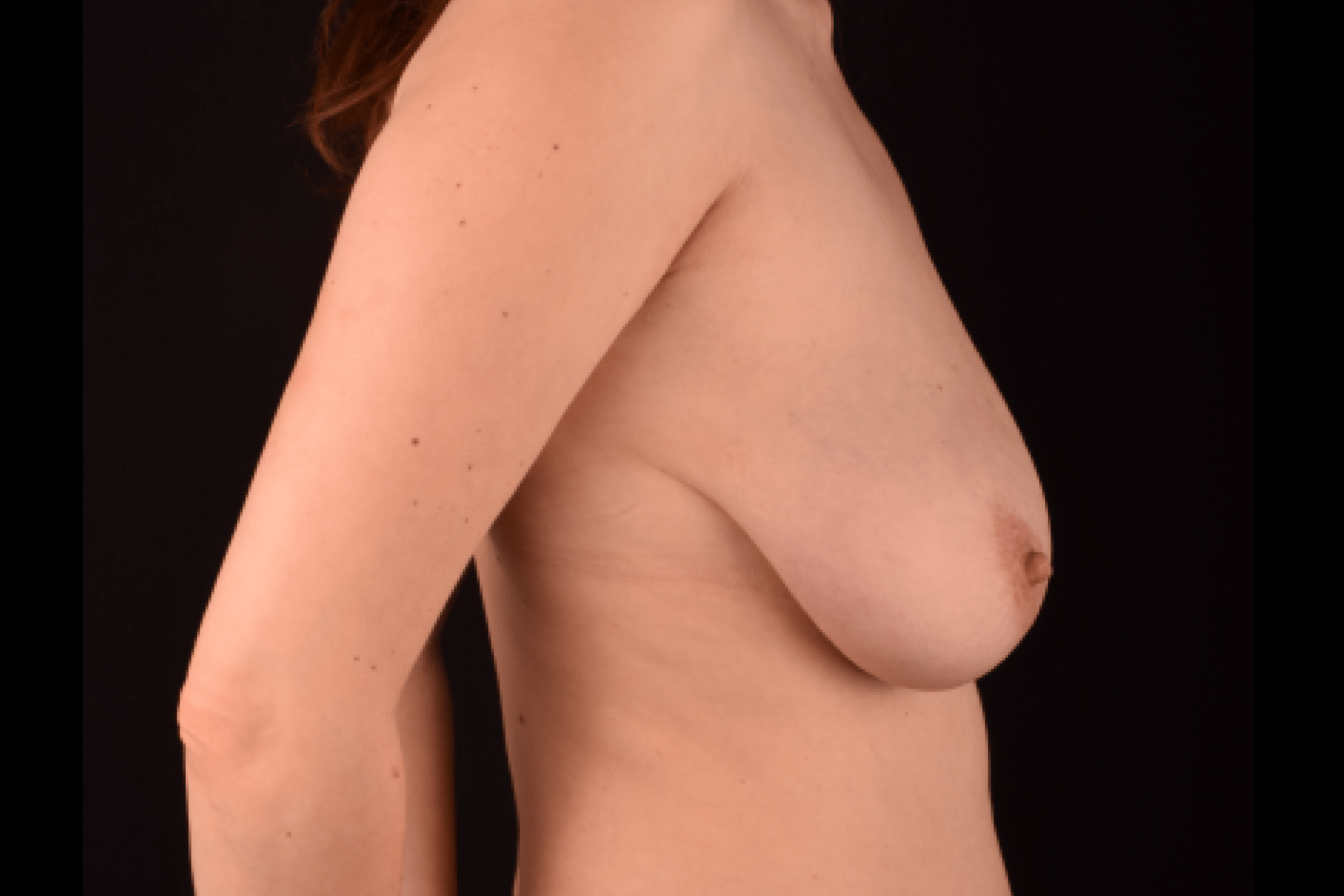
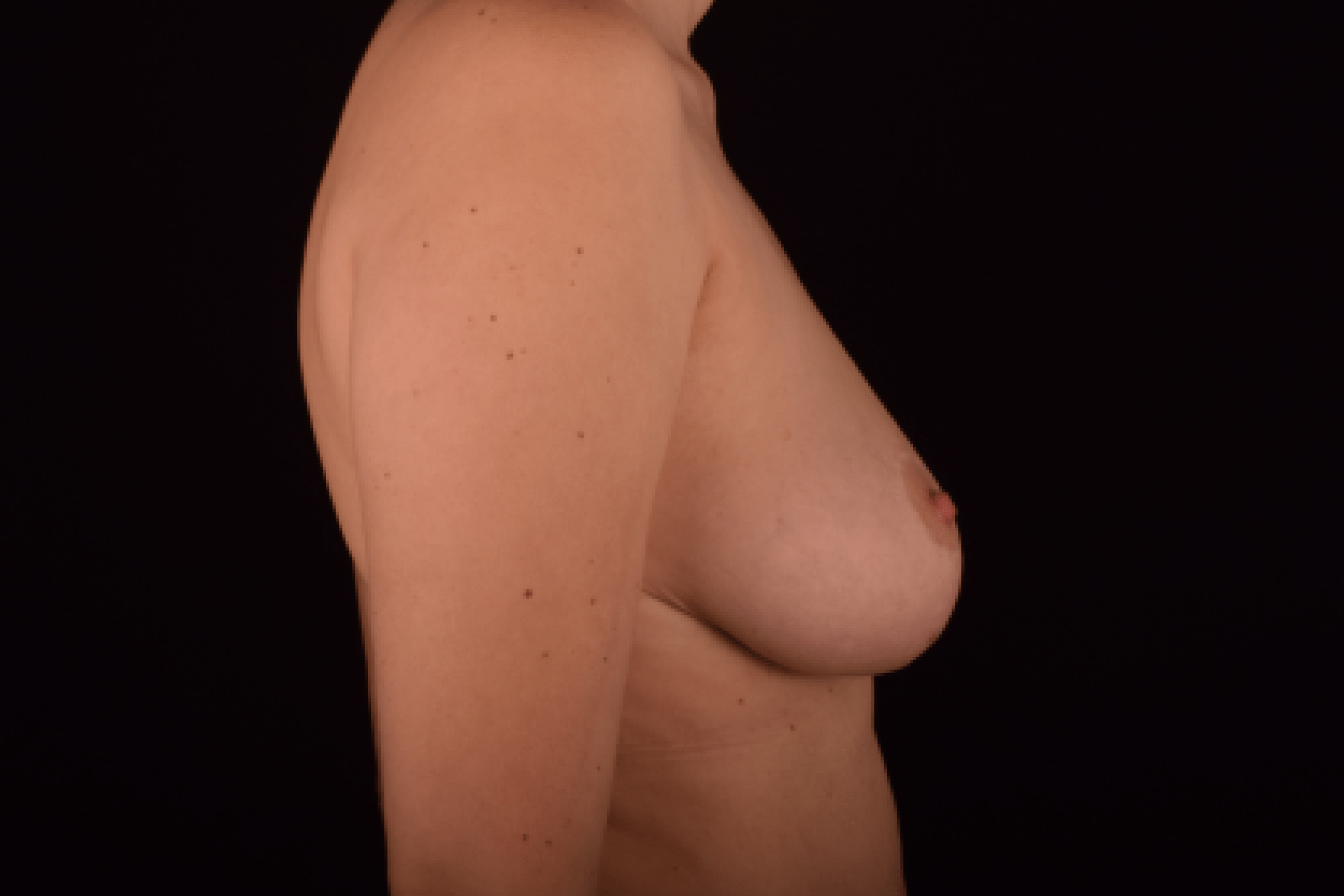
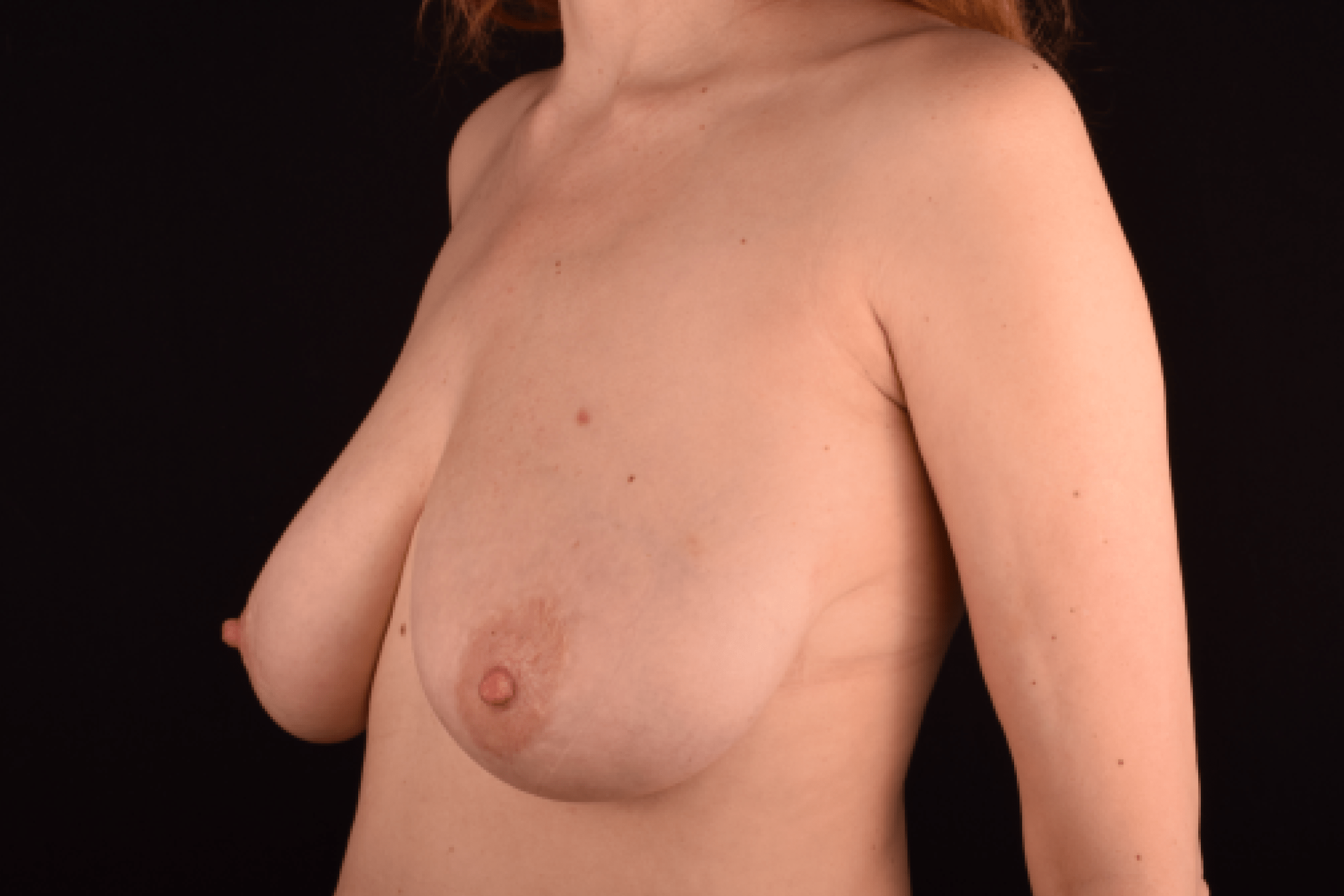
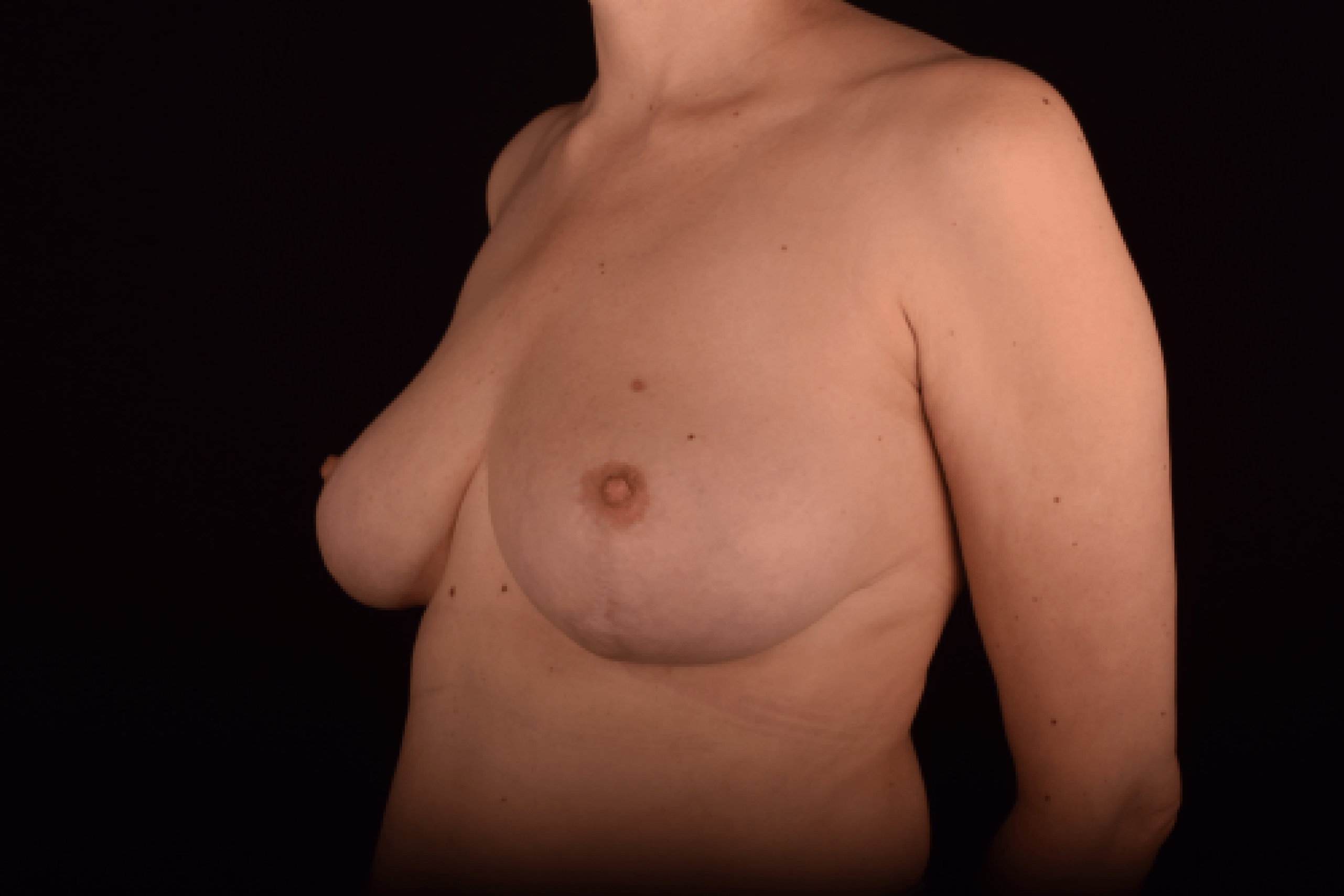
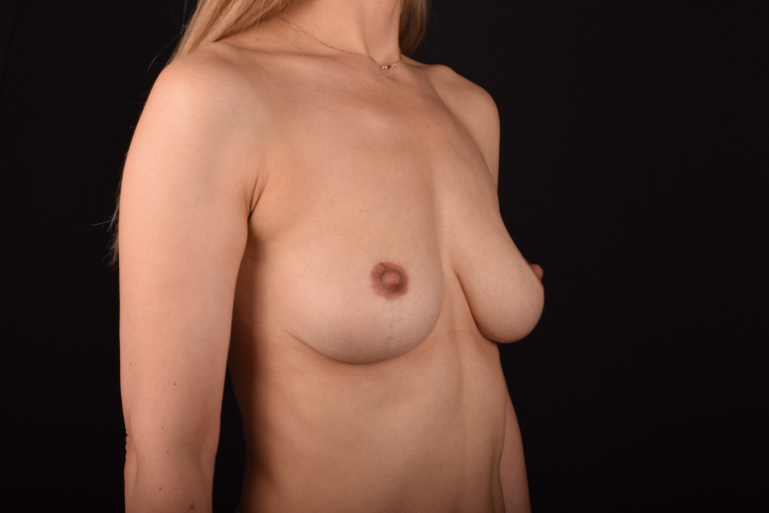
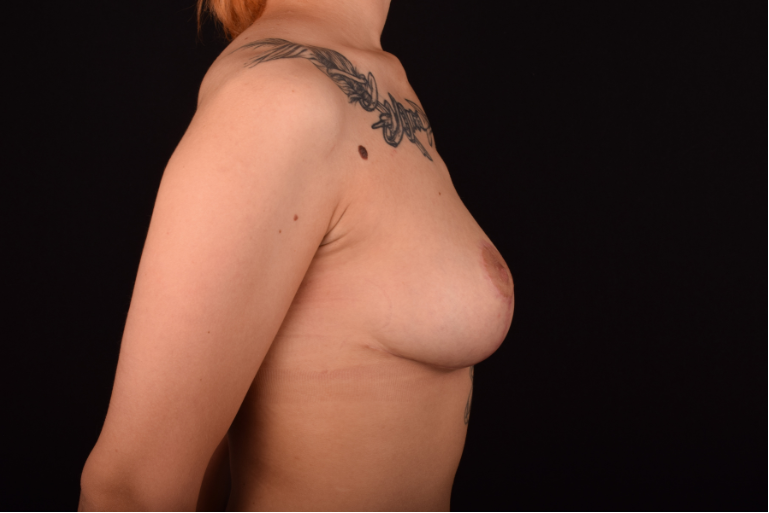
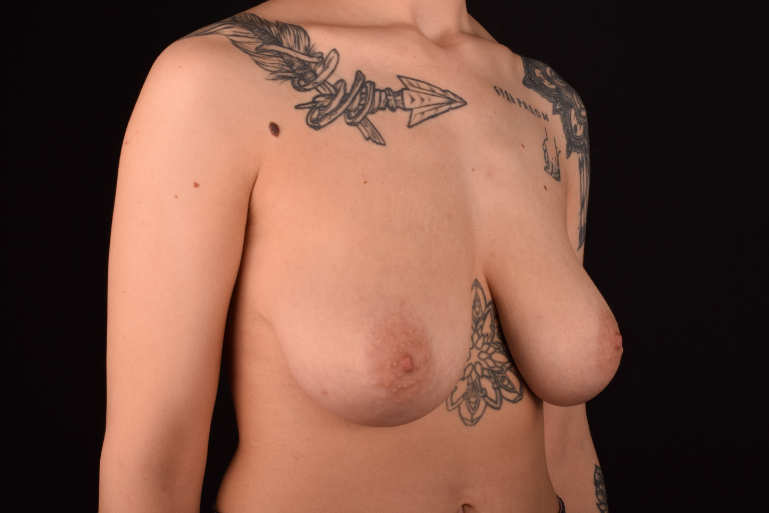
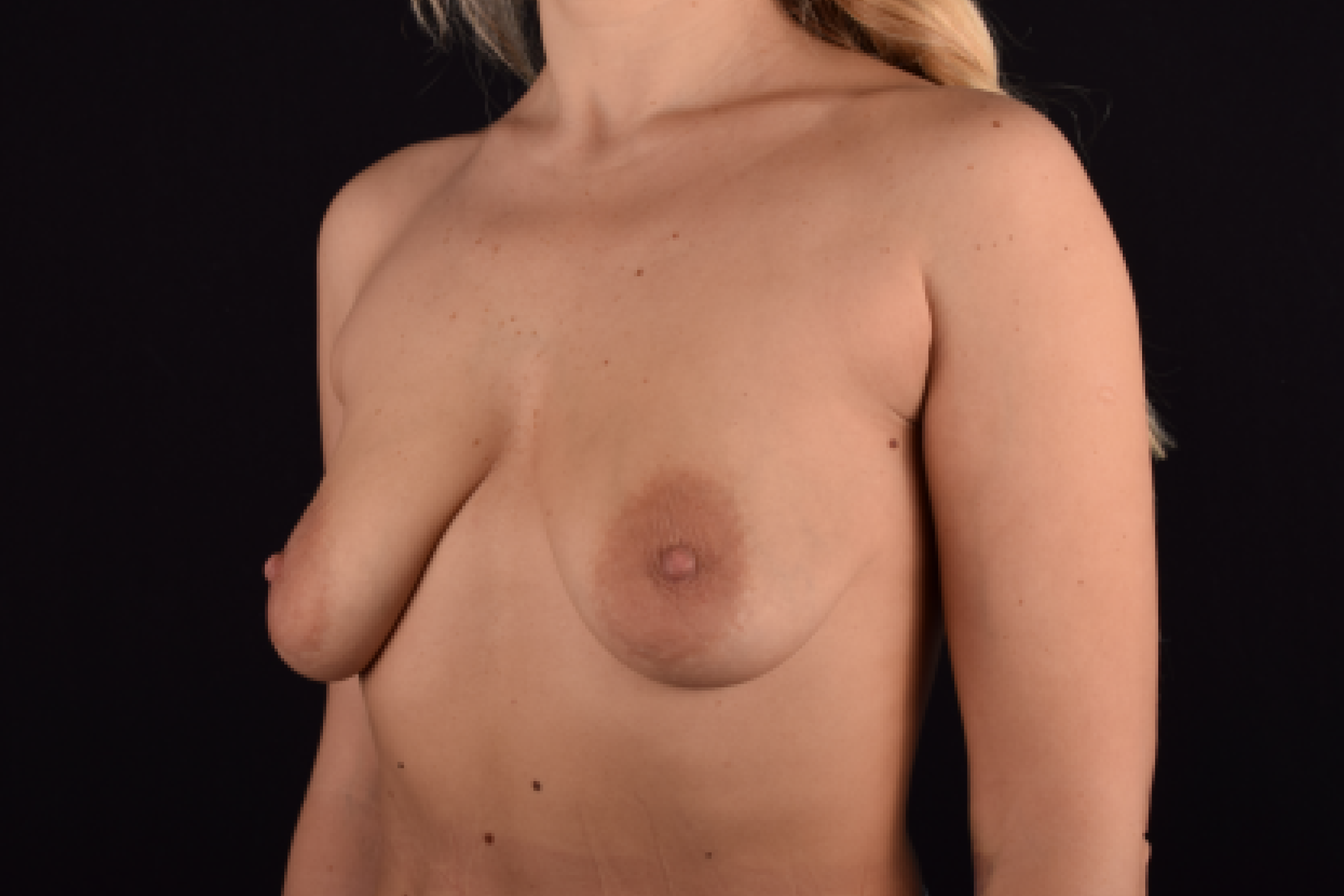
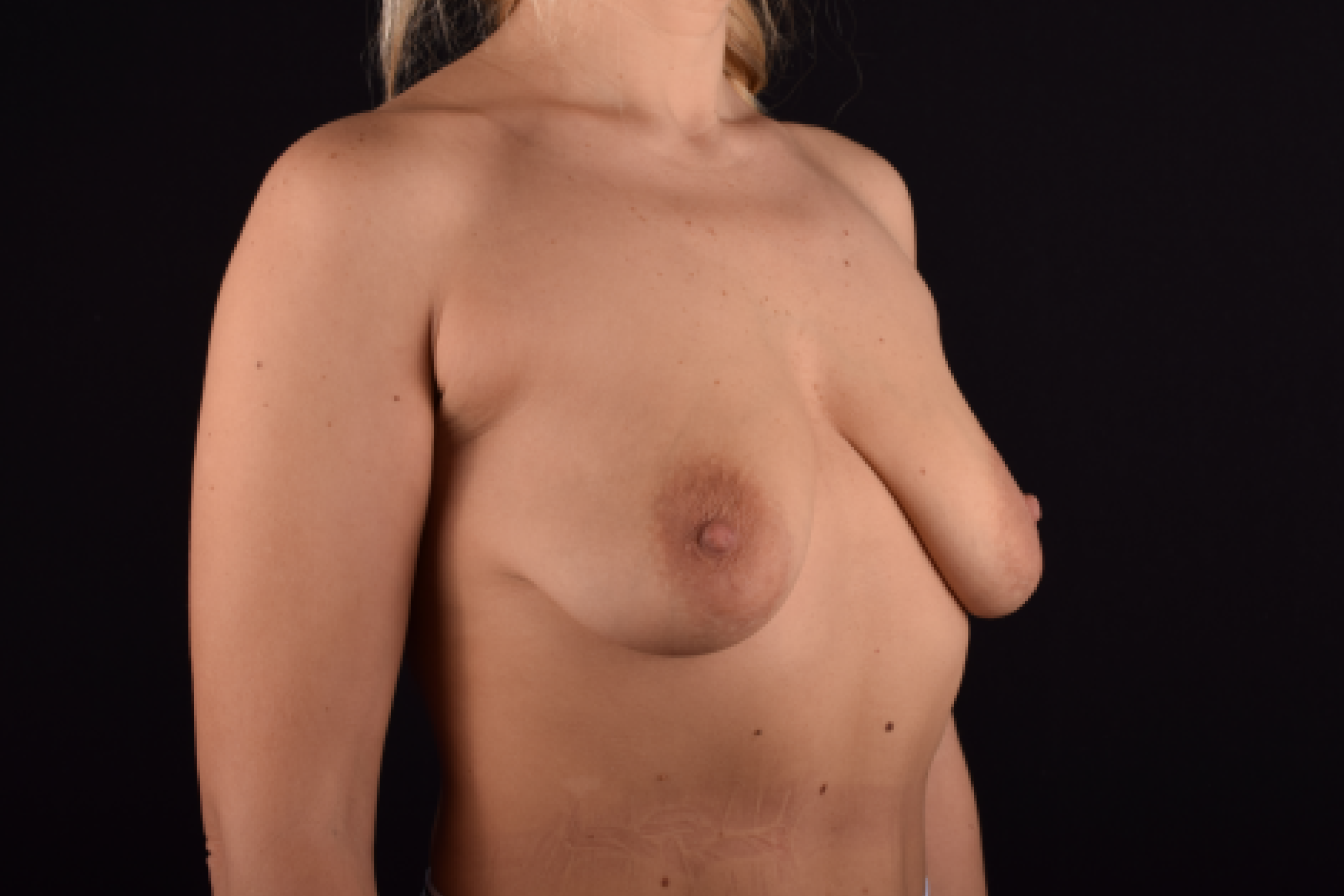
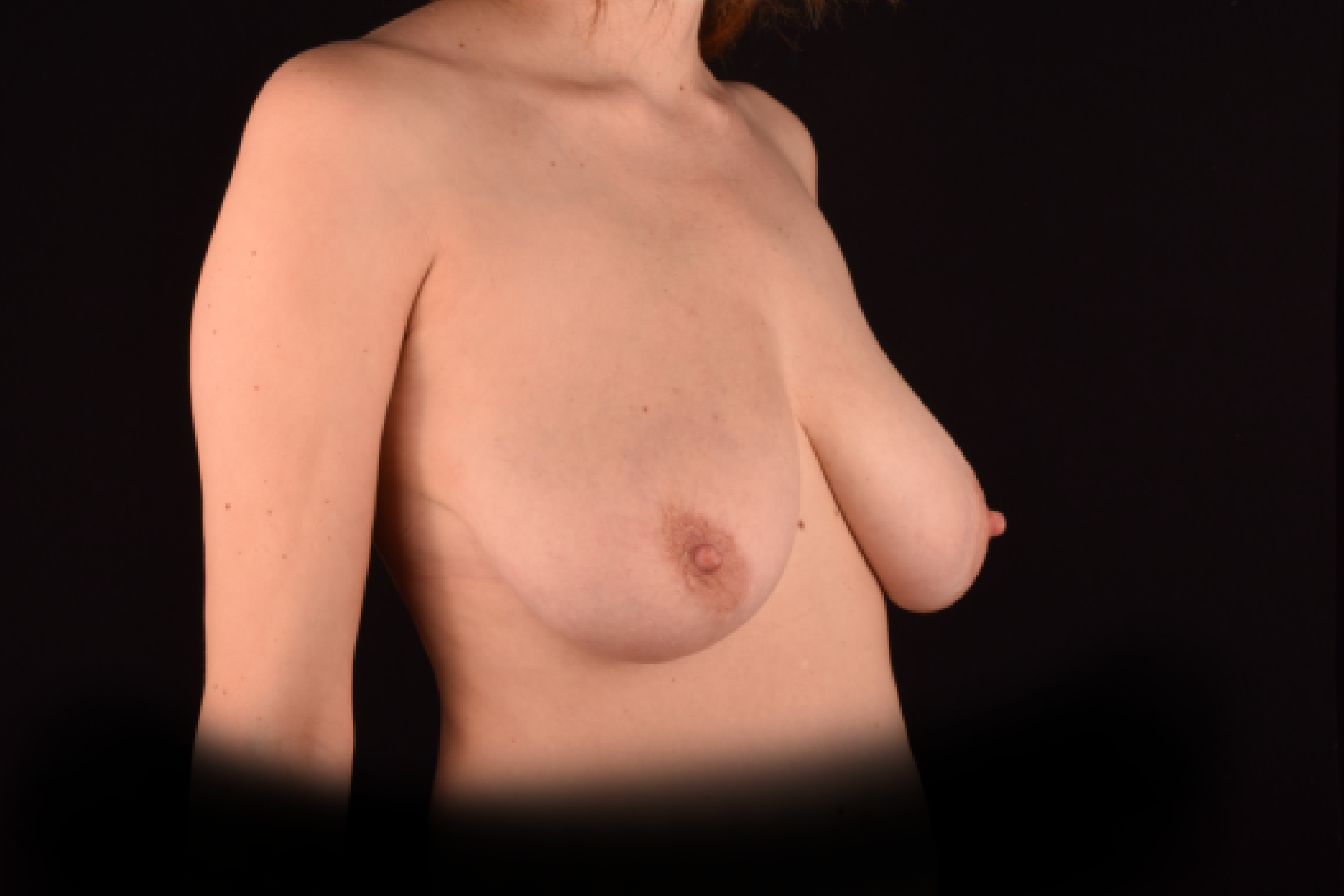
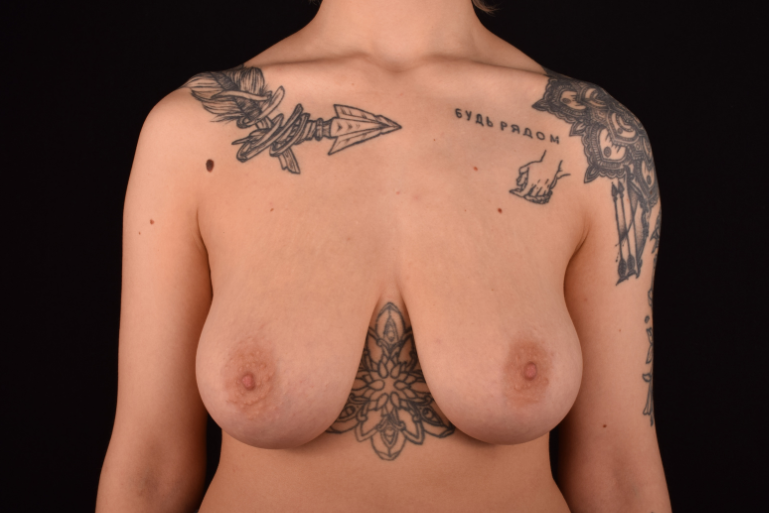
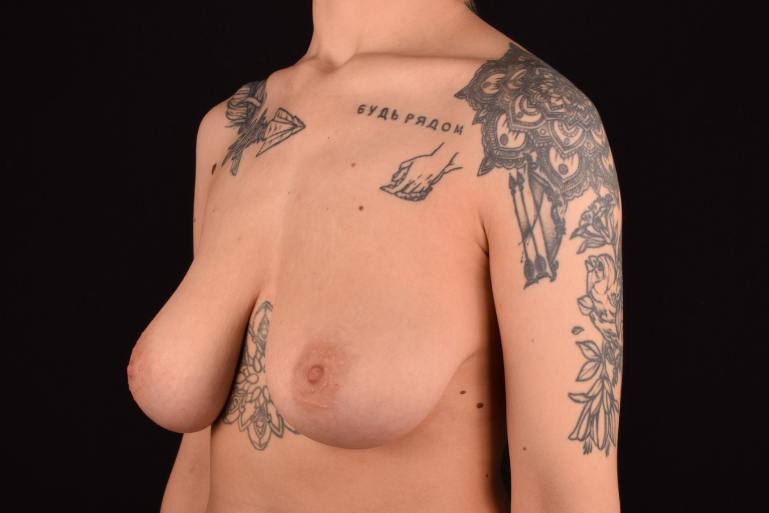
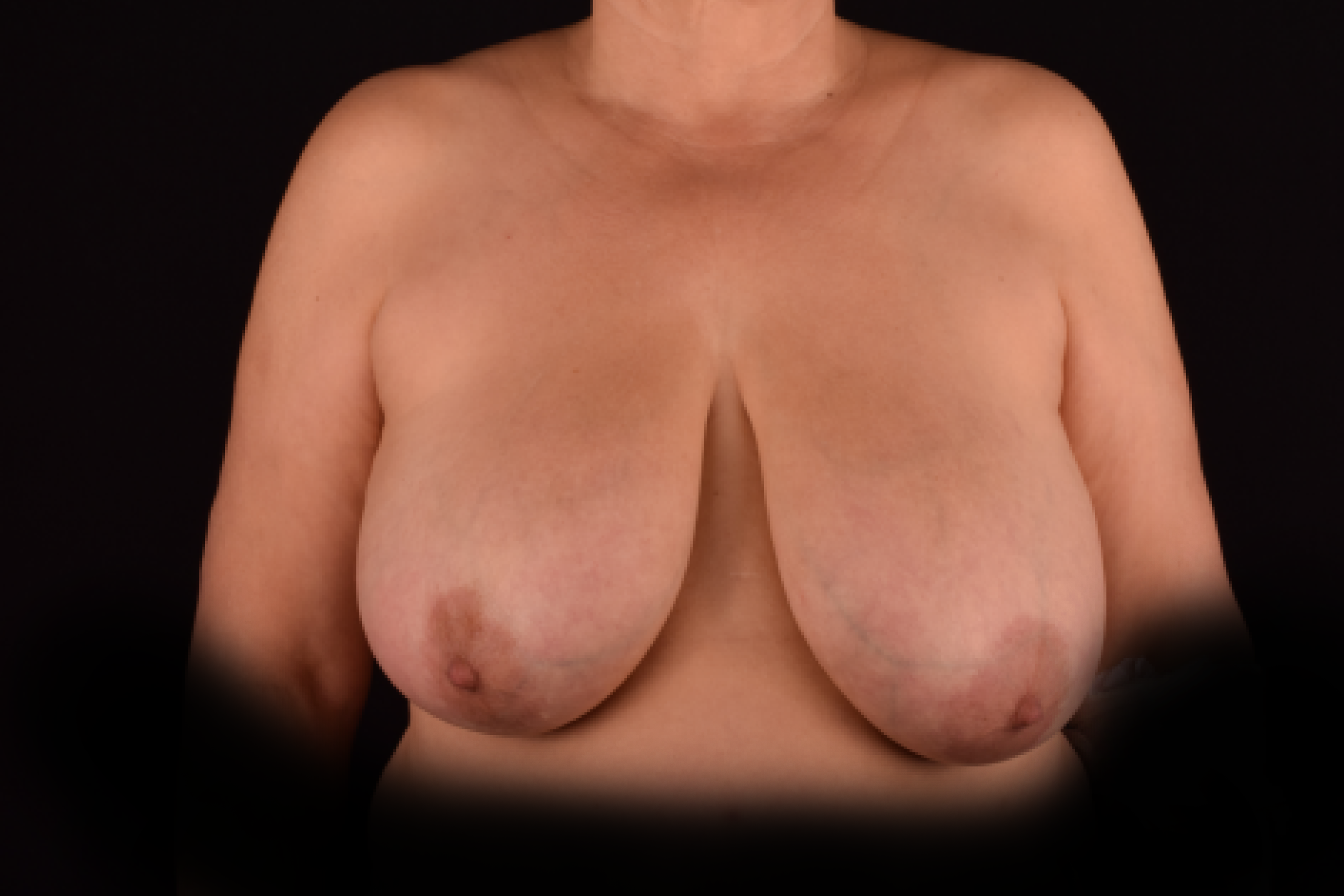
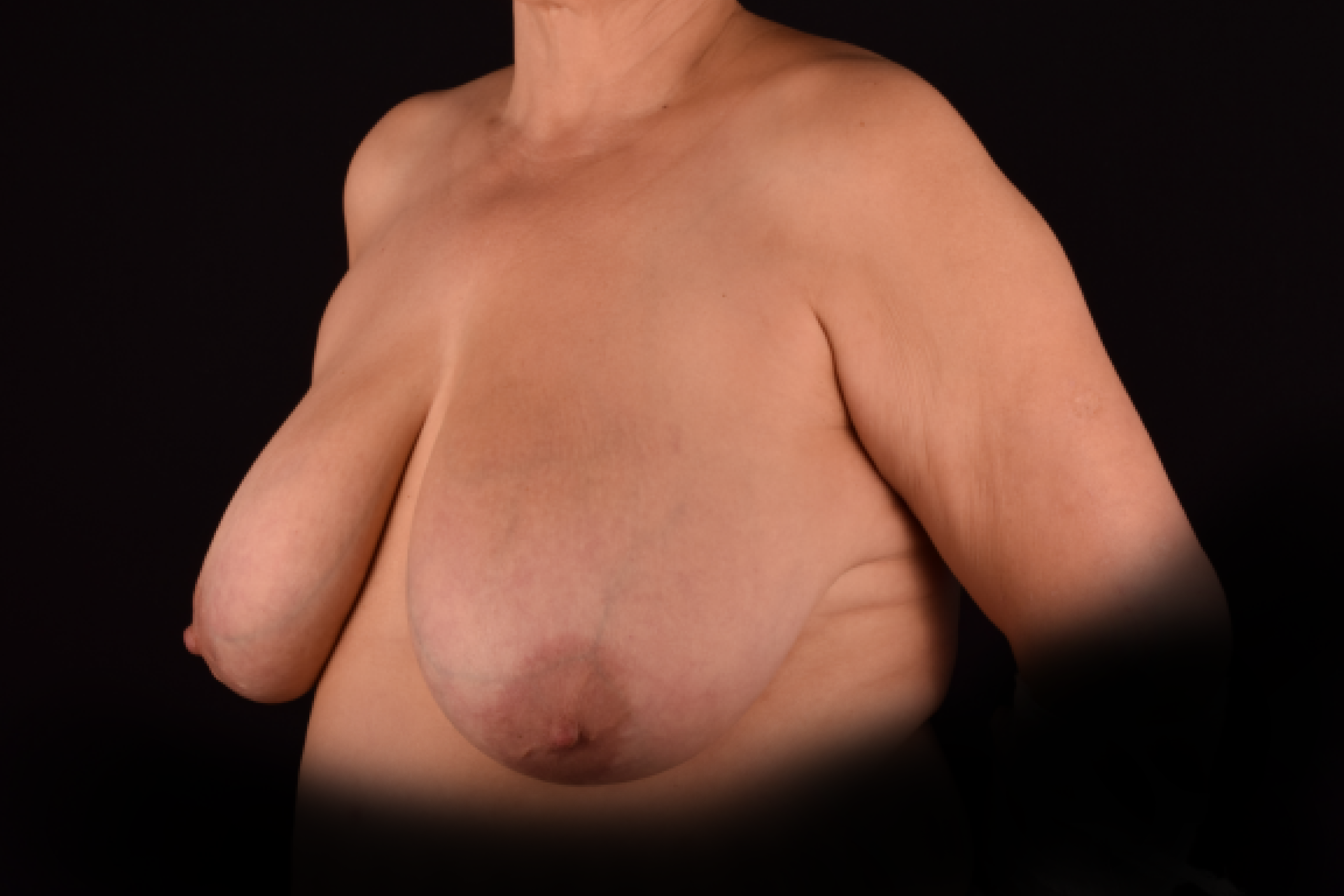
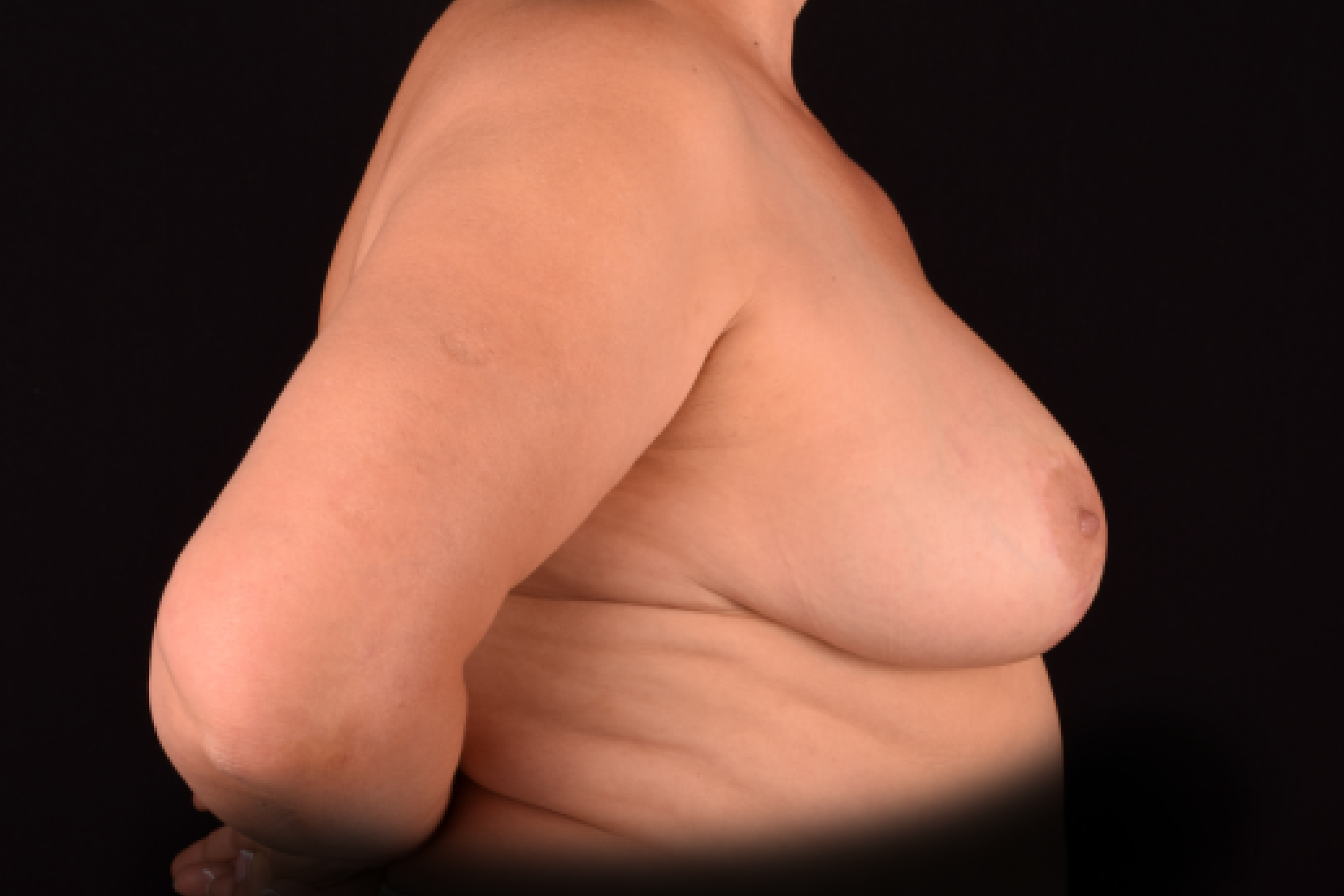
The degree of ptosis is determined by the position of the nipple-areolar complex on the hemisphere of the breast tissue. The lower the nipple is located relative to the inframammary (under the breast) fold, the more expressed the ptosis is.
Indications for mastopexy
The surgery is carried out with the following purpose:
- To elminate breast sagging.
- To set the normal breast hight.
- To get rid of breast asymmetry.
- To reshape and support the breast contour.
- To keep the breast tissues sensation.
- To save the lactation function (if possible).
General contraindications: mastopathy, cancer, cardiovascular and acute infectious diseases, chronic hypertensive disease, thyroid disorders, diabetes mellitus, blood-clotting disorder, under-age patients, high hyperadiposis (obesity), pre-arranged pregnancy, recent lactation.
Types of mastopexy
Depending on size, shape and the extent of breast sagging, there are four types of mastopexy (breast lift):
- Peri-areolar mastopexy is performed for small or medium-sized breasts with minimal or moderate ptosis. The incision is made at the junction of the breast skin and the areola, along the upper contour of the crescent-shaped areola.
- Circum-areolar mastopexy is used for slightly expressed ptosis, when you need to remove larger amount of skin (larger than while peri-areolar lifting) and lift the nipple more than 2 cm higher. The scar is located around the areola (Benelli method).
- Vertical mastopexy is suitable for various degrees of ptosis and stretched skin excess. It includes two types of incisions – the one around the areola and the vertical one from the areola to the inframammary fold (Benelli-Lollipop method).
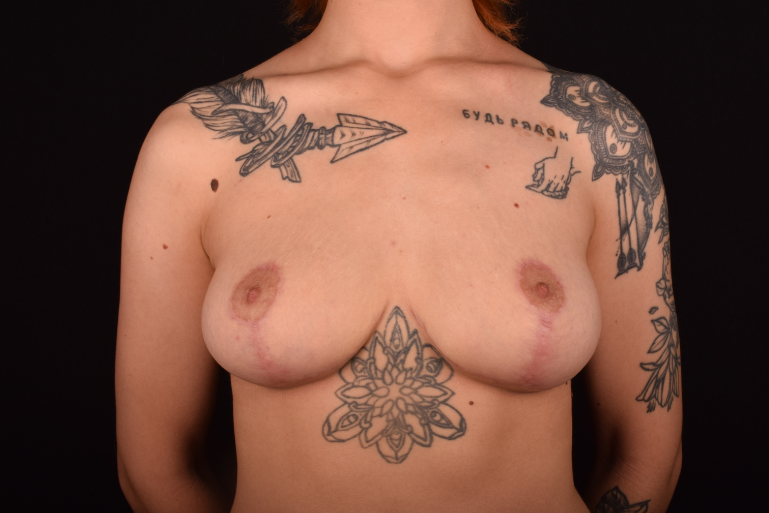
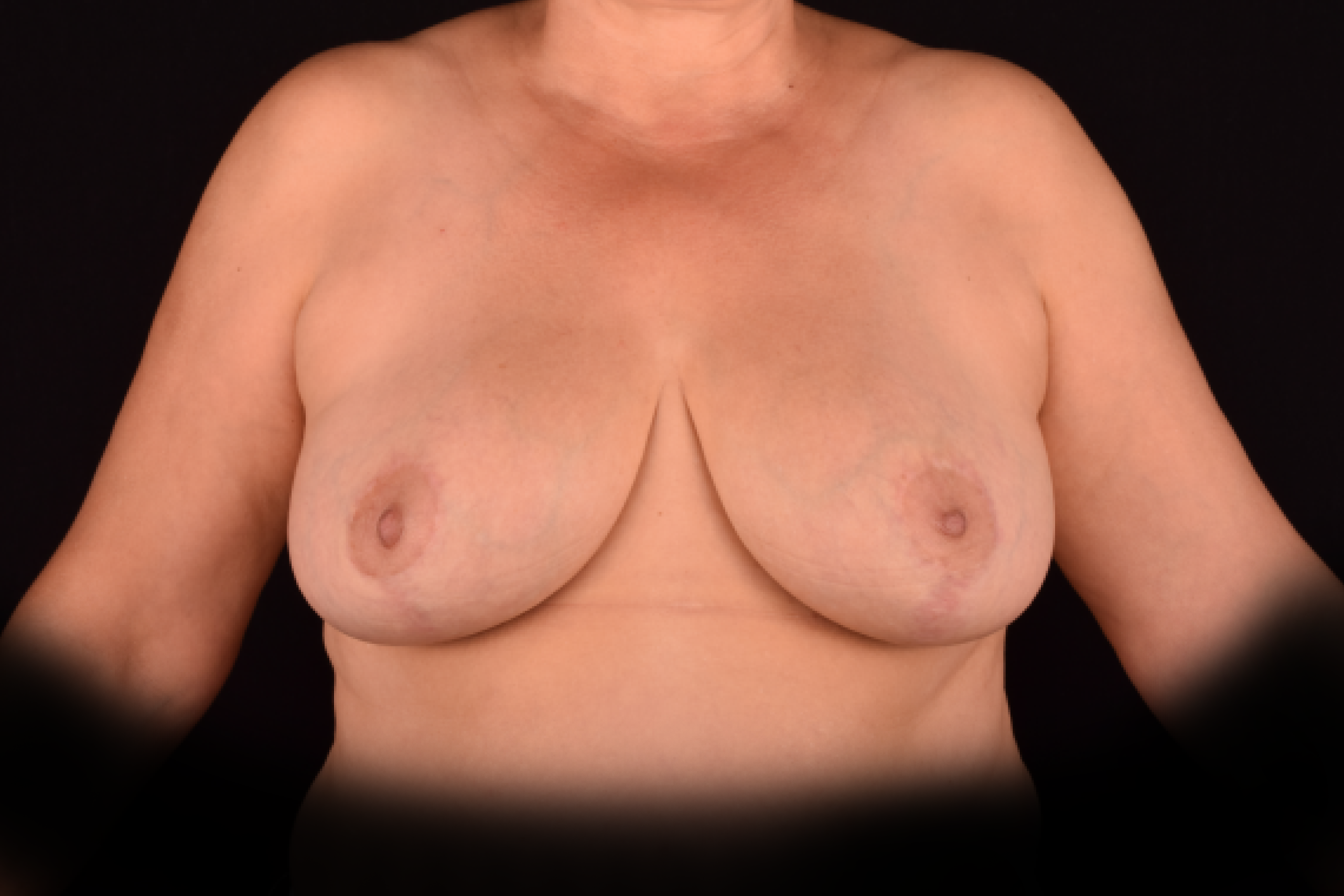
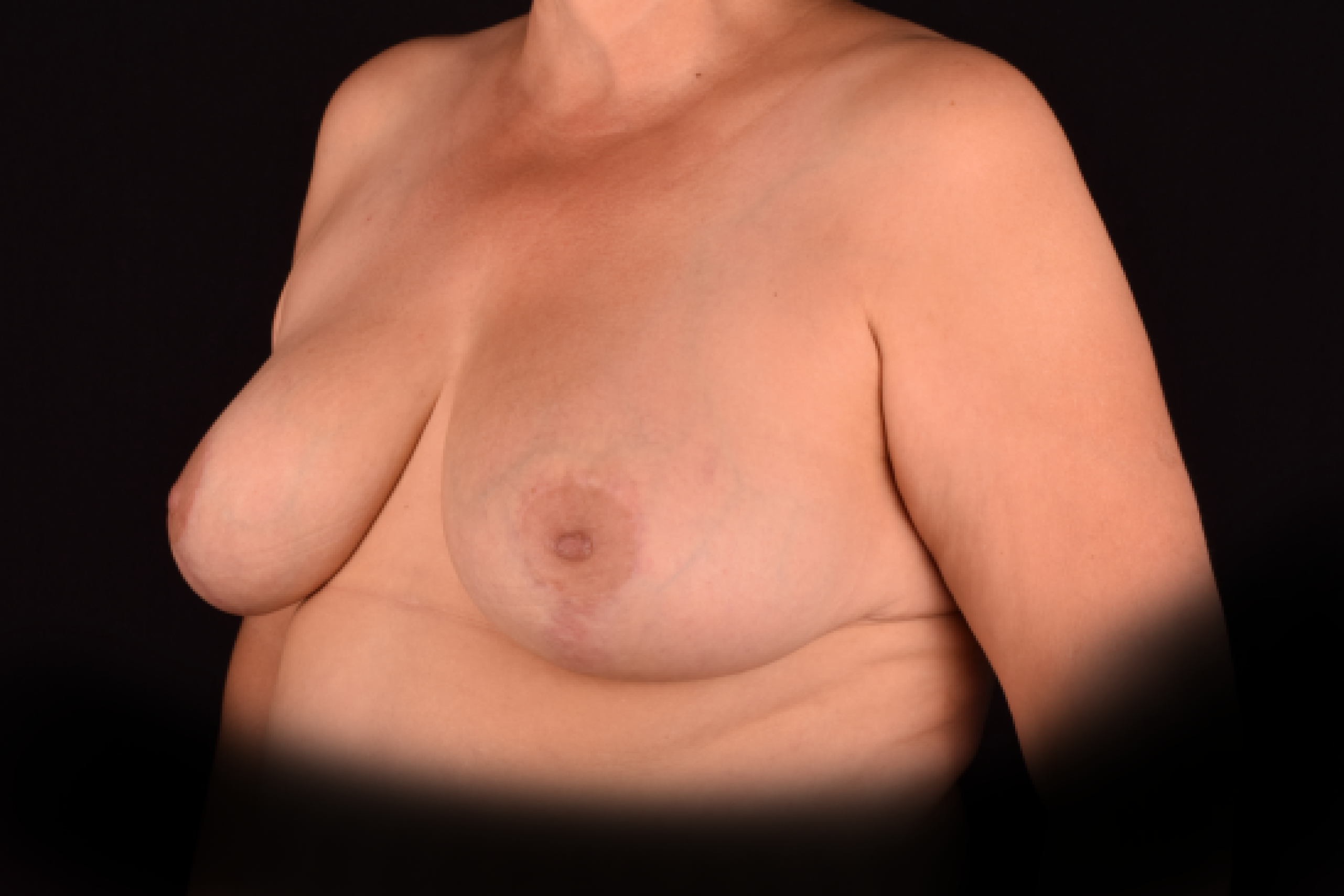
- T-shaped (anchor) mastopexy is indicated for patients with severe breast ptosis and involves incisions around the areola with vertical and horizontal components.
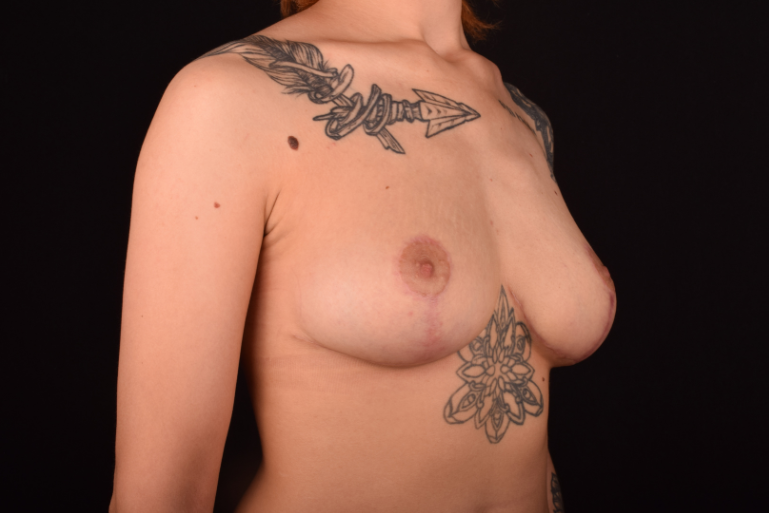
The postoperative scar has the shape of the inverse letter “T” or an anchor.
How is the surgery performed in “Certus” clinic?
Pre-surgery examination: 1 hour.
Duration of the surgery: 2-3 hours (depending on the complexity of the surgery). The patient stays in a clinical setting for 1-3 days.
Anaesthesis: general anesthesia or local anesthesia with sedating medications.
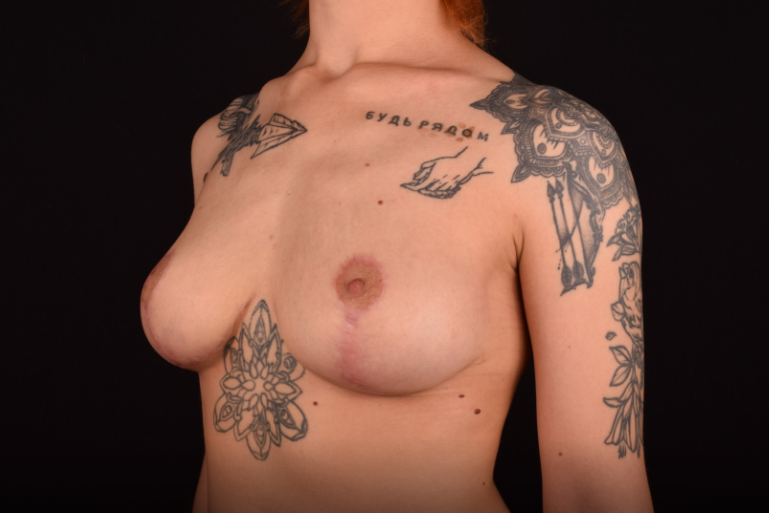
Incision options: the insicion is made around the areola with a vertical or T-shaped component. The incision options and the size of the removed breast tissues depend on the breast sagging extent (ptosis). The process of scars healing takes 6-12 months, after which they are hardly noticeable.
*Recovery period. After the surgery the patient wears special compression garments for 4-6 weeks. The stitches are removed on day 7-14. The swells and bruises disappear in a few weeks. The final formation of the mammary glands take place in 3-4 months after the surgery.
*Side effects: temporary bruises, swelling, reduced breast sensation, slight soreness.
*Risks: infectious complications, hematomas, sustainable healing process, poor (asymmetric) scarring, reduced nipple, areoles or breast sensation; asymmetry of breast’s shape and size, deformation of the breast contours, the capsular contracture formation, loss of breastfeeding possibility.
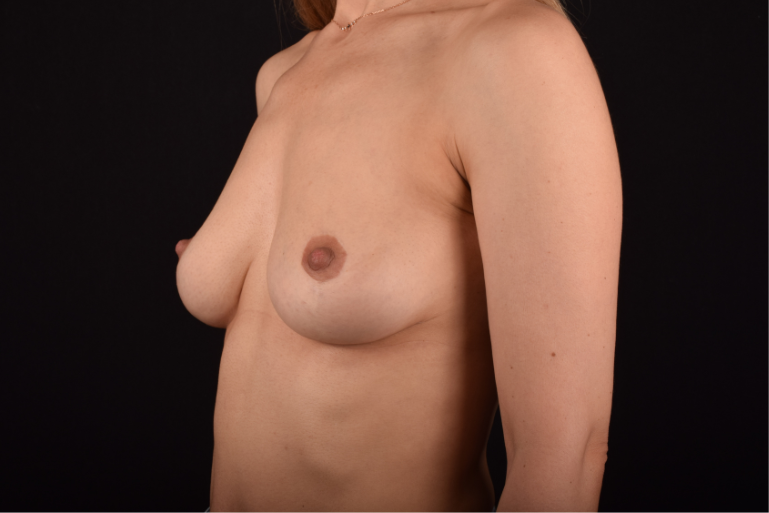
*Result is long-term. Pregnancy, aging, weight fluctations can lead to the subsequent breast sagging.
*The effect, result, risks, and recovery period depend on the individual peculiarities of the human body.






























Add review