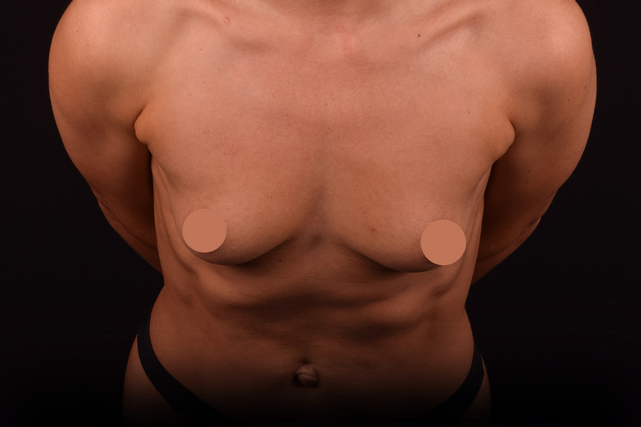
Indications for Mammoplasty
- Small, underdeveloped breasts.
- Post-lactation mammary glands involution.
- Birth defects of the breast (reconstructive or cosmetic mammaplasty).
- Mammary glands asymmetry (Breast asymmetry).
General contraindications: mastopathy, cancer, cardiovascular and acute infectious diseases, chronic hypertensive disease, thyroid disorders, diabetes mellitus, blood-clotting disorder, under-age patients, high hyperadiposis (obesity), pre-arranged pregnancy, recent lactation.
Types and characteristics of breast implants.
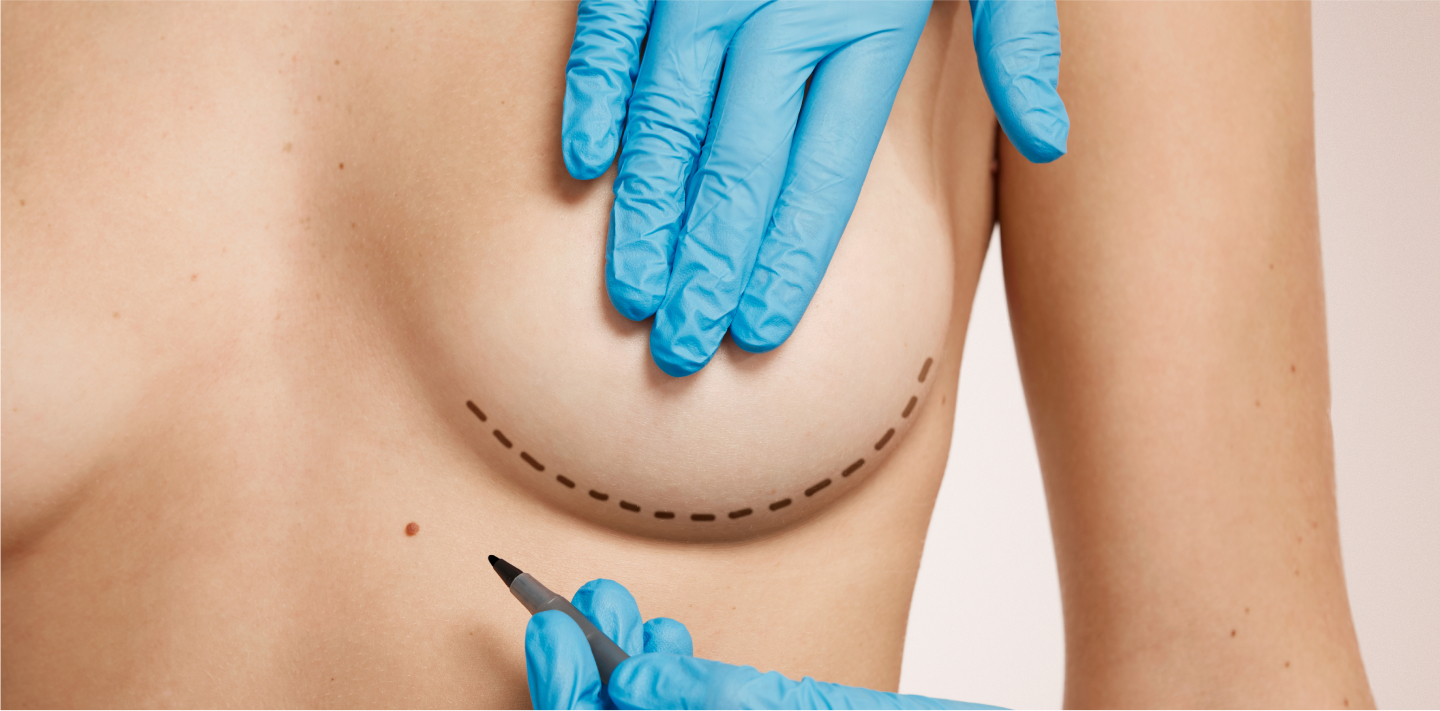
Surgical breast augmentation is performed using breast implants or mammary glands endoprosthesis. Implants differ by shape, volume, projection, filler and surface texture.
There are round shaped and antomical (drop shaped) implants available. A round implant makes the breast’s upper pole more filled. The anatomical implant has the shape of a drop and gives the breasts more natural look.
Types of breast implants according to their filler.
- Silicone breast implants are filled with higly cohesive silicone gel. It has the shape memory, it doesn’t leak if the implant shell breaks. Such implants are inserted with a lifetime warranty, as they do not deform over time.
- Saline breast implants are filled with sterile salt water, thereby the surgery is performed through a smaller incision. Such implants are subjected to replacement as they lose shape over time.
- Biocompatible gel implants are filled with natural polymer, obtained from cellulose which when collapsed will be absorbed and naturally expelled by the body.
There are breast endoprostheses with a smooth and textured shell surface. The latter reduce the risk of capsular contracture formation – this happens when a tissue capsule, which occurs naturally around the implant, becomes too tight and begins to squeeze it, which can cause deformation of the breast contour. With a textured implant, the capsule grows into the texture of its shell.
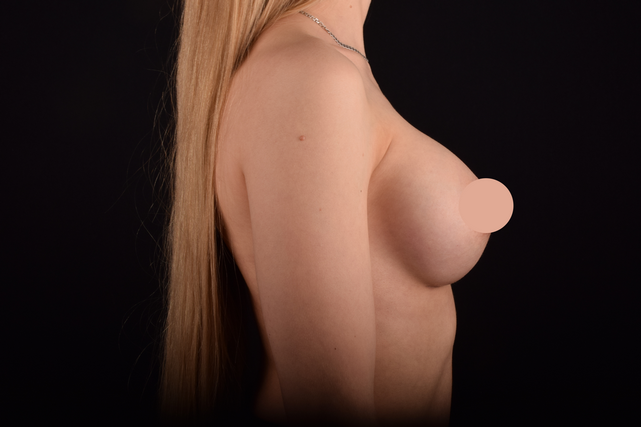
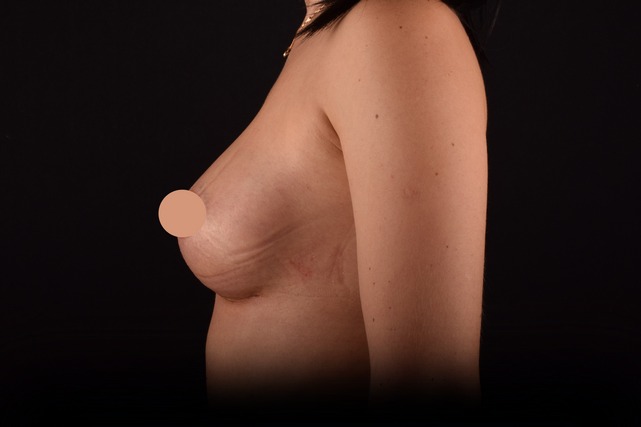
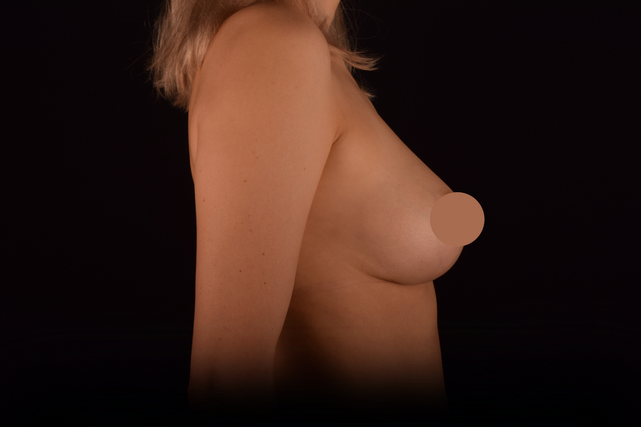
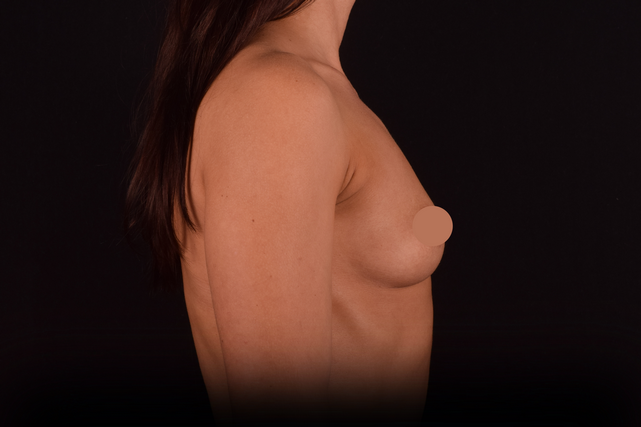
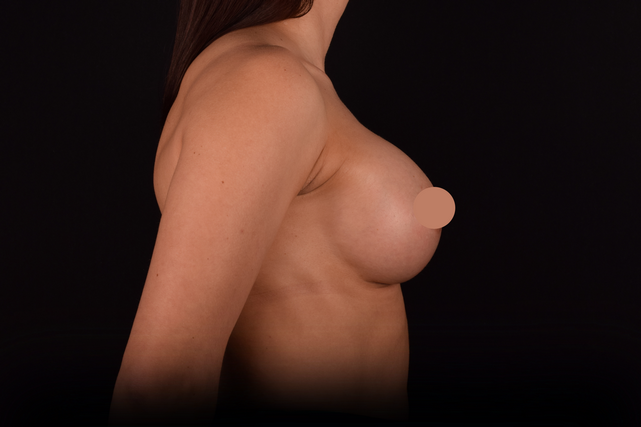
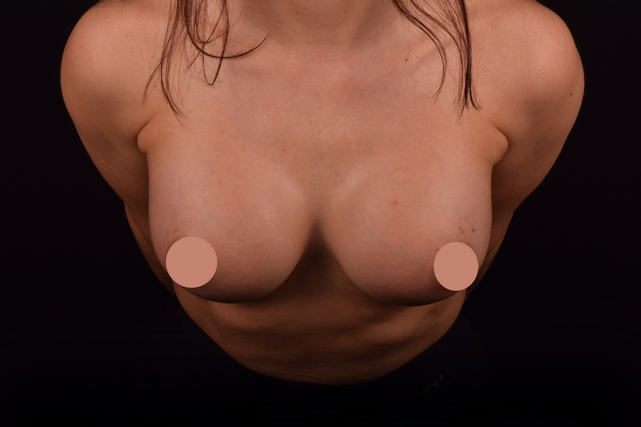
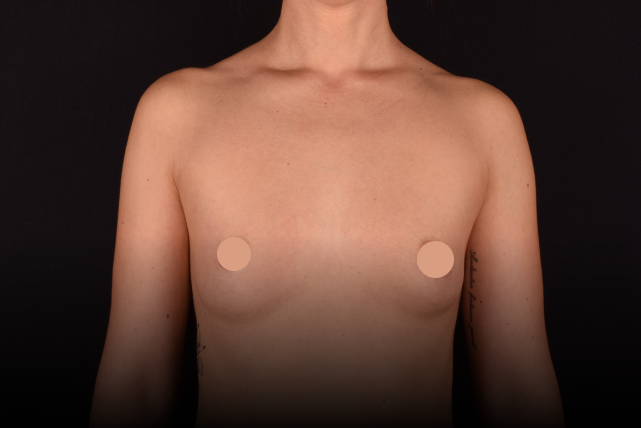
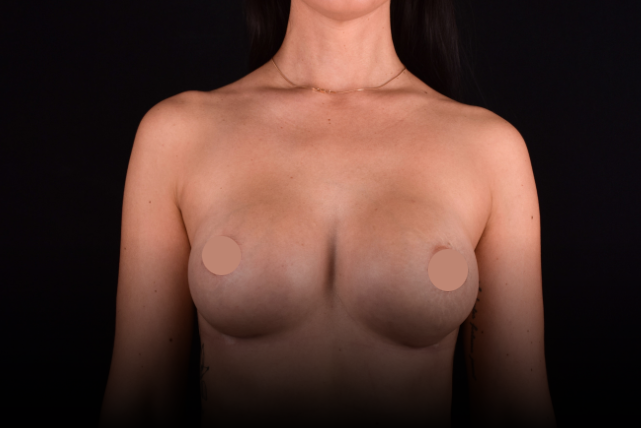
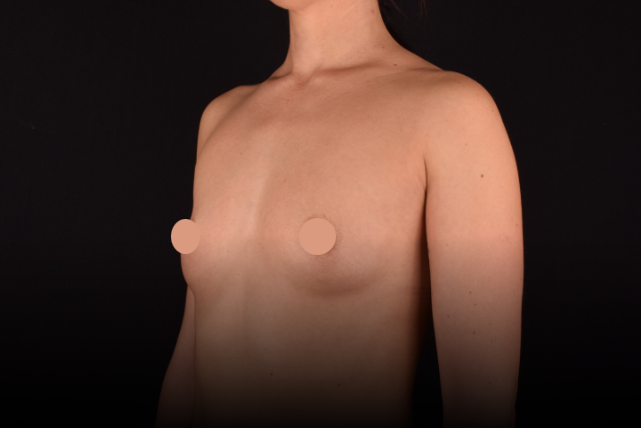
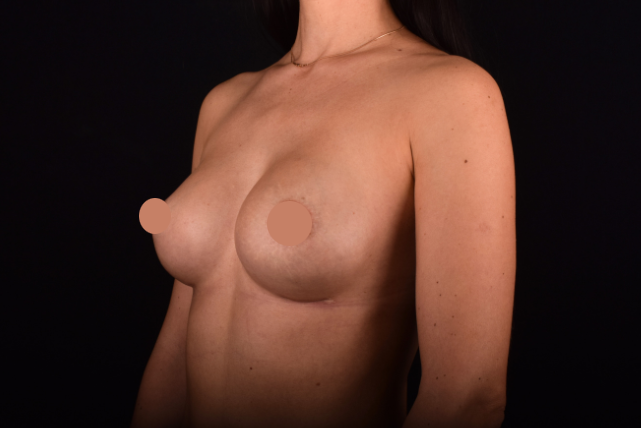
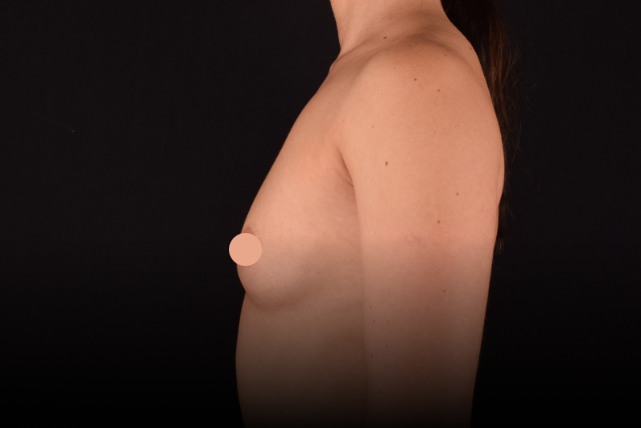
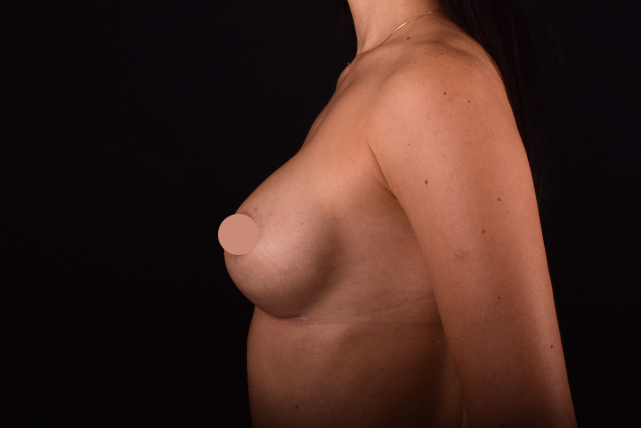
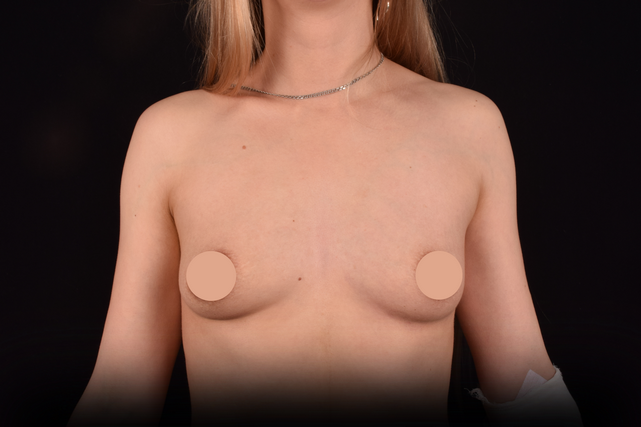
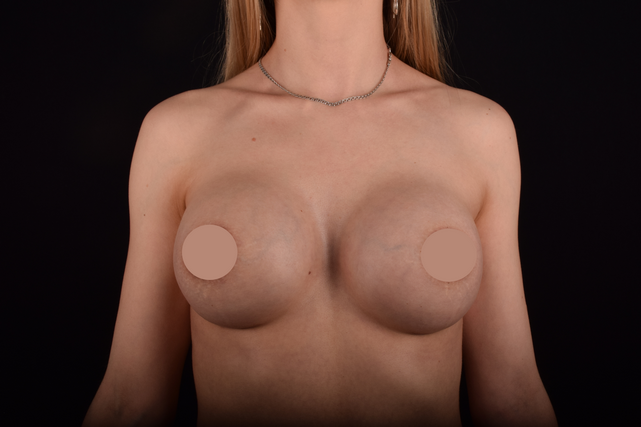
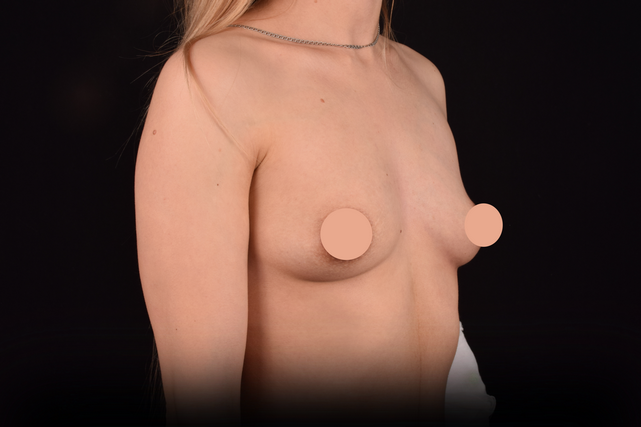
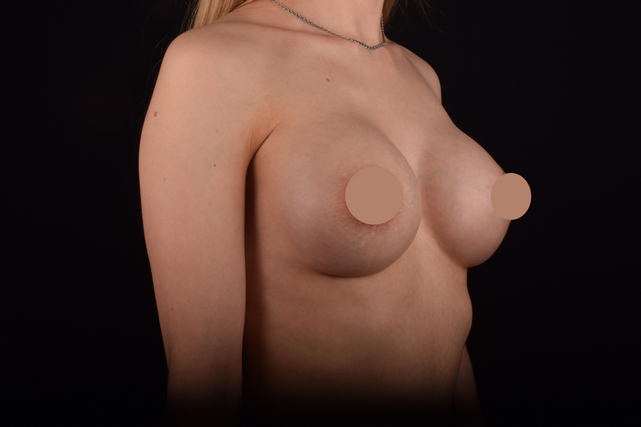
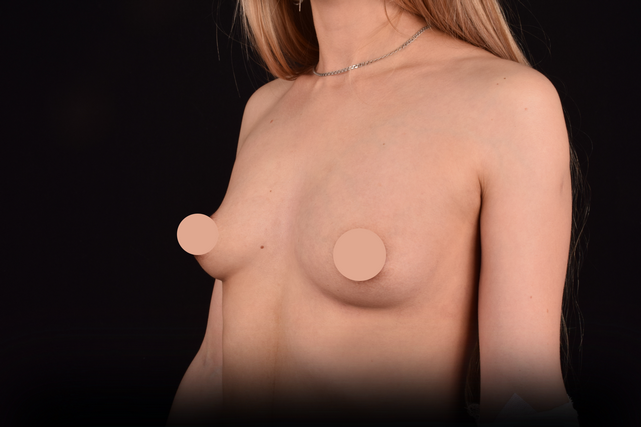
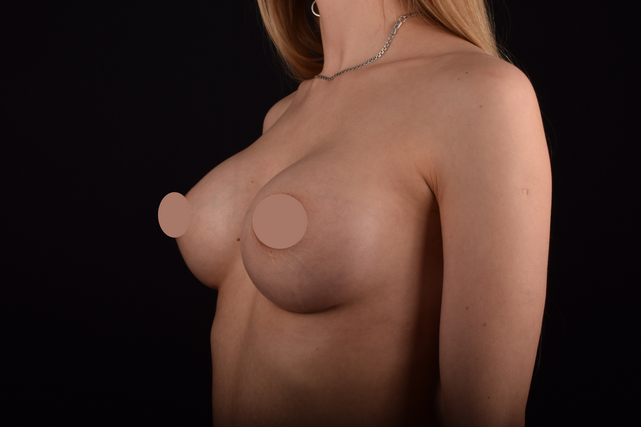
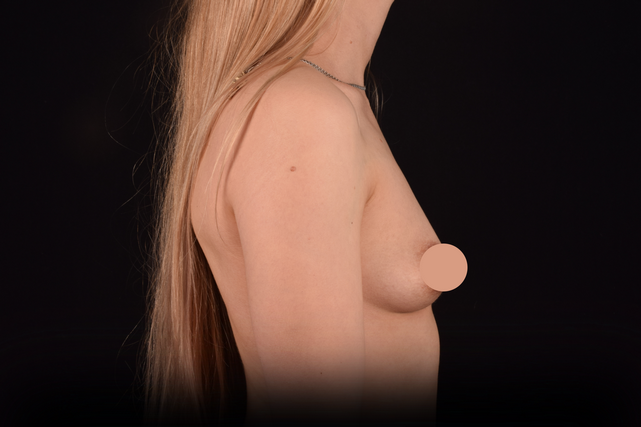
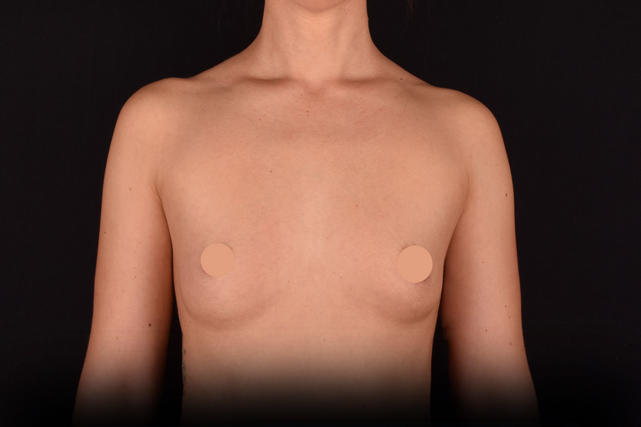
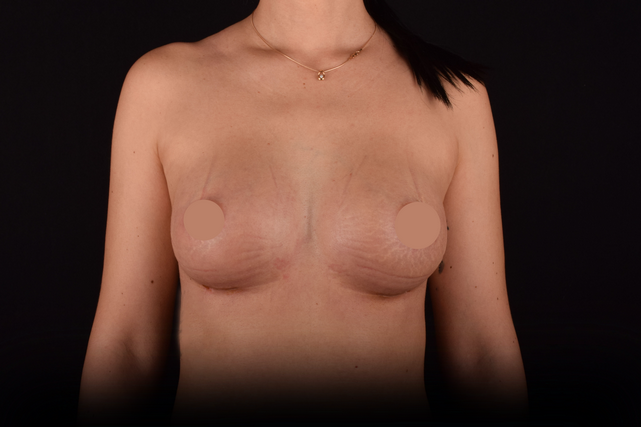
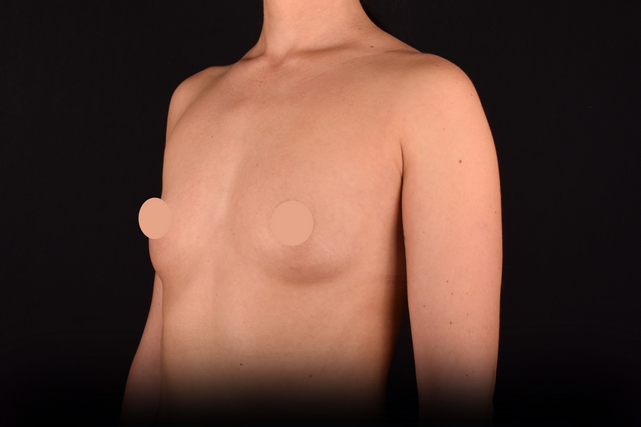
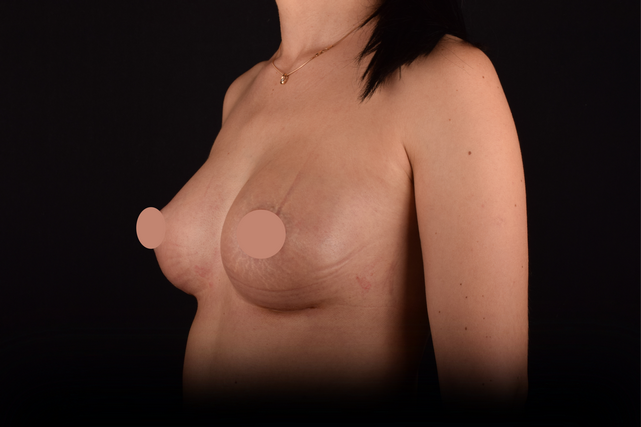
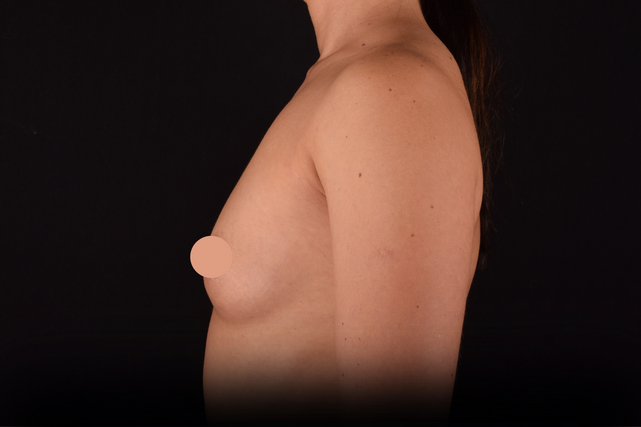
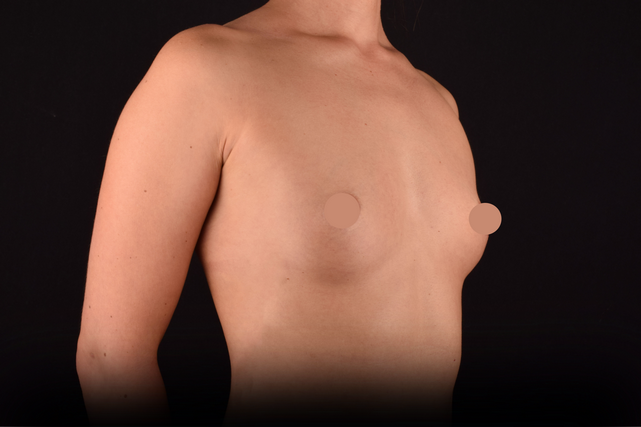
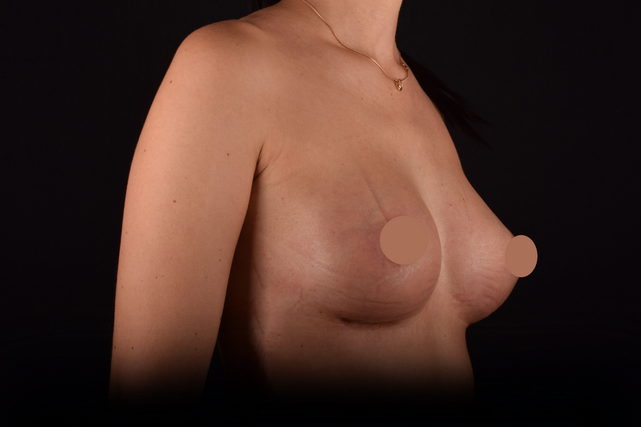
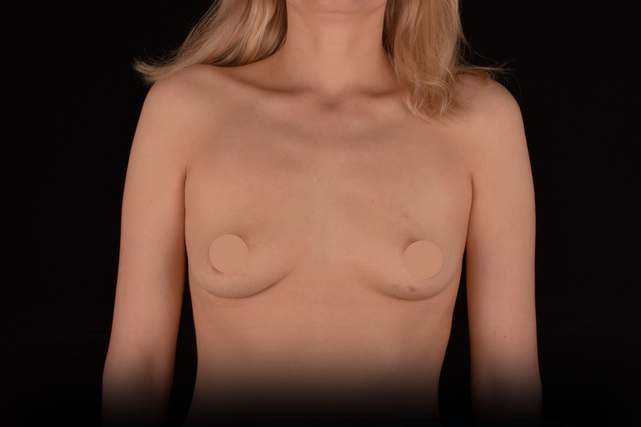
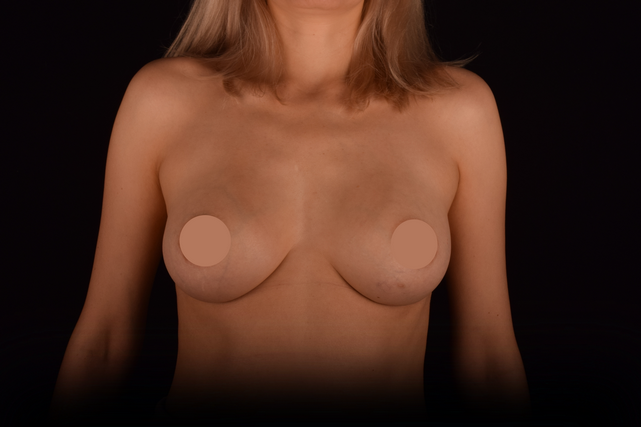
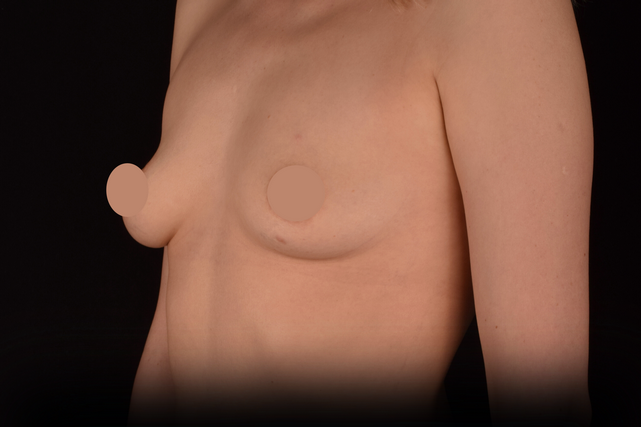
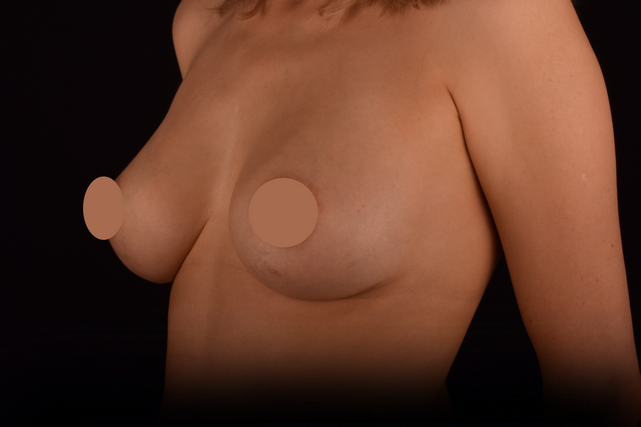
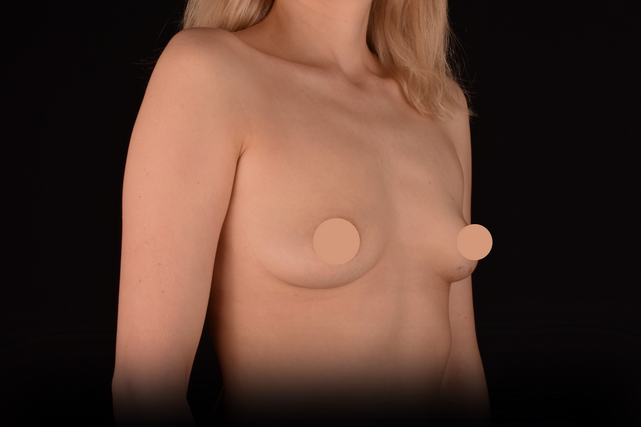
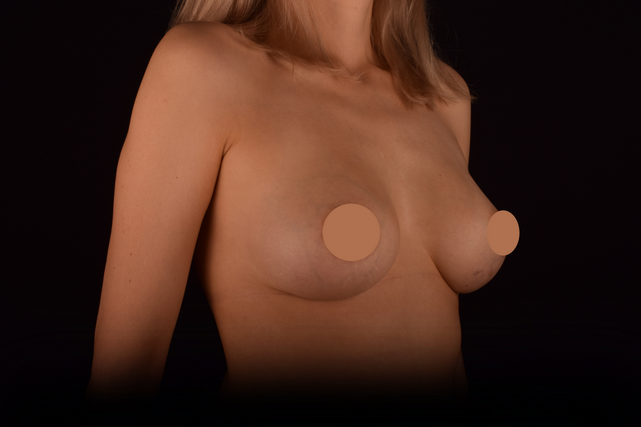
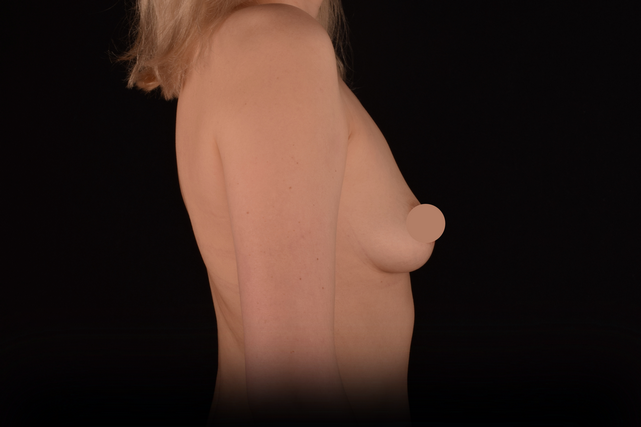
Mammaplasty before / after
Implants placement
Here are some most common places where breast implants are inserted when breasts are augmented.
- Retromammary space (behind the breast tissue). This position of the endoprosthesis does not violate the integrity of the breast, which eliminates the possibility of emerging pathologies.
- The area under the pectoral muscle. This is the most acceptable area for very skinny patients, because if they are given implants directly behind the breast tissue, the implants will be strongly felt through the skin.
Accessions (incisions through wich endoprostheses are inserted):
- Peri-areolar access (along the nipple-areolar complex) – the incision is made along the lower contour of the areola to minimize visible scarring after the surgery. The disadvantage of this access is that the integrity of the breast tissue is violated. This can lead to breastfeeding complications. This technique is used for women who have already given birth.
- The armpit access (axillary incision) is performed under the pectoral muscle, mainly for those patients who have the mild subcutaneous fatty tissue.
- In the inframammary fold – the fold under the breast. It is the most convenient way to carry out visual inspection and ensure maximum reliability and results predictability.
- A belly-button approach – used during abdominoplasty (plastics, tummy tuck).
How is the surgery performed in “Certus” clinic?
Pre-surgery examination: 1-3 days.
Duration of the surgery: 1-2 hours (depending on the complexity of the operation). The patient stays in a clinical setting for 1-3 days.
Anaesthesis: general anesthesia.
Incision options: along the areolar edge (peri-areolar incision), the fold under the breast (inframammary fold) and in the armpit (axillary incision). A breast implant is inserted into a pocket either under the pectoral muscle (a submuscular placement) or directly behind the breast tissue, over the pectoral muscle (inframammary/ subglandular placement). The process of scars healing takes 6-12 months, after which they are hardly notable.
*Recovery period. After the surgery the patient wears special compression garments for 4-6 weeks. The sutures are removed in 7-14 days. The swells and bruises disappear in a few weeks. The final formation of the mammary glands occurs in 3-4 months after the surgery.
*Side effects: temporary bruises, swelling, reduced chest sensation, slight soreness.
*Risks: infectious complications, hematomas, sustainable healing process, poor (asymmetric) scarring, reduced nipple, areoles or breast sensation; asymmetry of breast’s shape and size, deformation of the breast contours, the capsular contracture formation, loss of breastfeeding possibility.
*Result is long-term.
Pregnancy, aging, weight fluctuations can lead to changes in the shape and size of the breast.
*The effect, result, risks, and recovery period depend on the individual peculiarities of the human body.



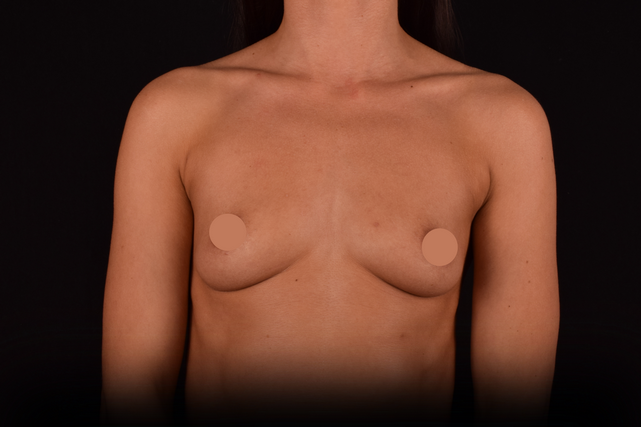
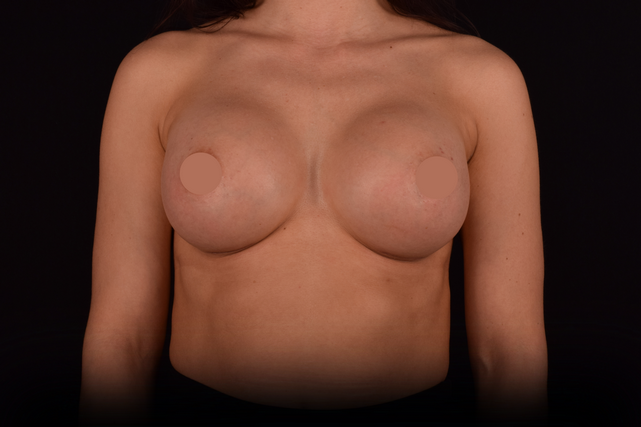
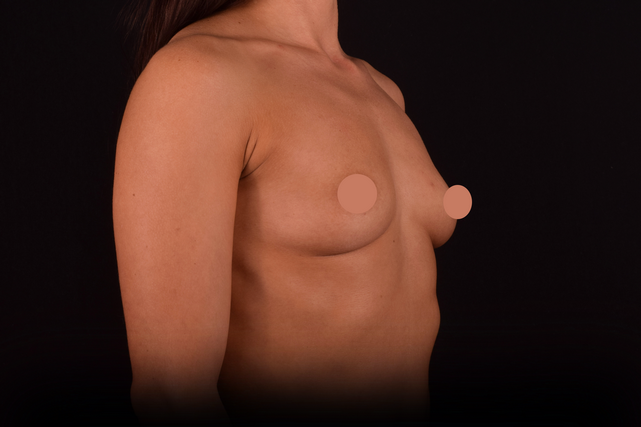
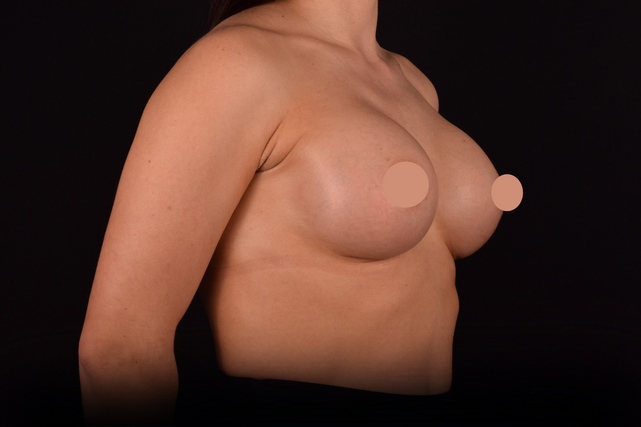

















Add review